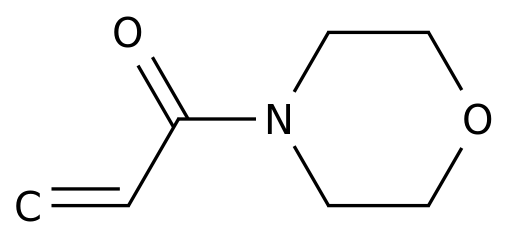
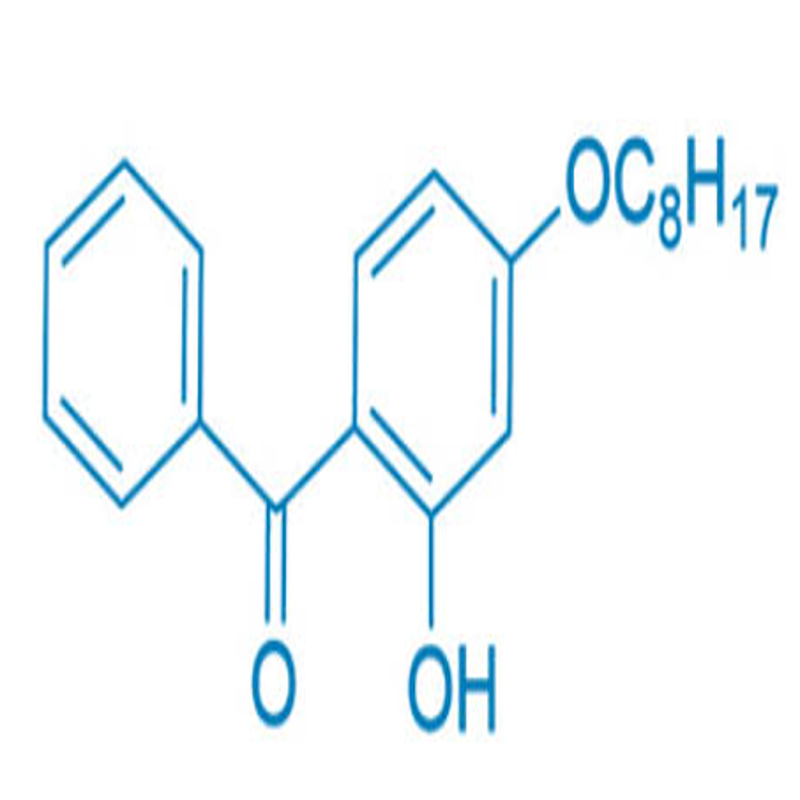
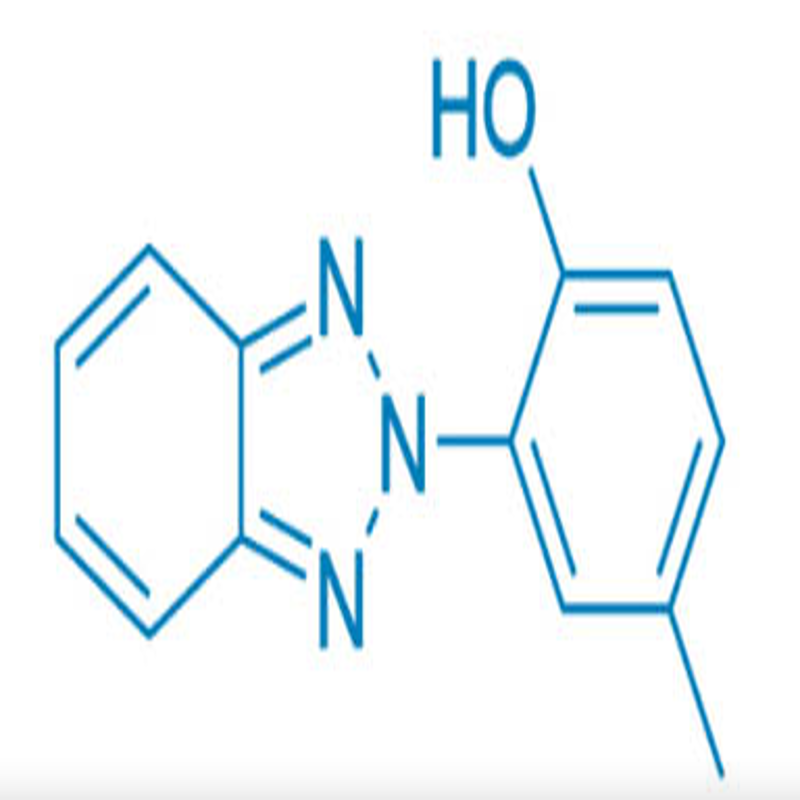
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
On May 16, the New York state environmental regulator unveiled a draft pollution regulation that would require the closure of remaining coal-fired power plants or the use of clean fuels such as natural gas to generate electricity
again by 2020.
The US state of New York has demanded the closure of all remaining coal-fired power plants by 2020
The New York State Environmental Protection Agency (NYDEC) said the rule will help the state meet the goal
set by Governor Andrew Cuomo to reduce carbon emissions by 40 percent by 2030.
According to New York State grid operators, nearly 3,000 megawatts of coal-fired generation capacity have been retired since 2000, leaving only 979 megawatts of capacity
by 2018.
One megawatt of capacity can power
about 1,000 homes.
Coal-fired power generation accounts for only about 2 percent
of New York State's total electricity generation of 39,064 megawatts.
Most of New York State's electricity comes from oil and gas (48%), nuclear (14%), hydropower (11%) and gas (10%)
.
This summer, New York's Independent System Operator (ISO) predicted that the state would have enough available resources to meet peak demand
of 32,904 megawatts.
,
On May 16, the New York state environmental regulator unveiled a draft pollution regulation that would require the closure of remaining coal-fired power plants or the use of clean fuels such as natural gas to generate electricity
again by 2020.
The US state of New York has demanded the closure of all remaining coal-fired power plants by 2020
The US state of New York has demanded the closure of all remaining coal-fired power plants by 2020The New York State Environmental Protection Agency (NYDEC) said the rule will help the state meet the goal
set by Governor Andrew Cuomo to reduce carbon emissions by 40 percent by 2030.
According to New York State grid operators, nearly 3,000 megawatts of coal-fired generation capacity have been retired since 2000, leaving only 979 megawatts of capacity
by 2018.
One megawatt of capacity can power
about 1,000 homes.
Coal-fired power generation accounts for only about 2 percent
of New York State's total electricity generation of 39,064 megawatts.
Most of New York State's electricity comes from oil and gas (48%), nuclear (14%), hydropower (11%) and gas (10%)
.
This summer, New York's Independent System Operator (ISO) predicted that the state would have enough available resources to meet peak demand
of 32,904 megawatts.
,