-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
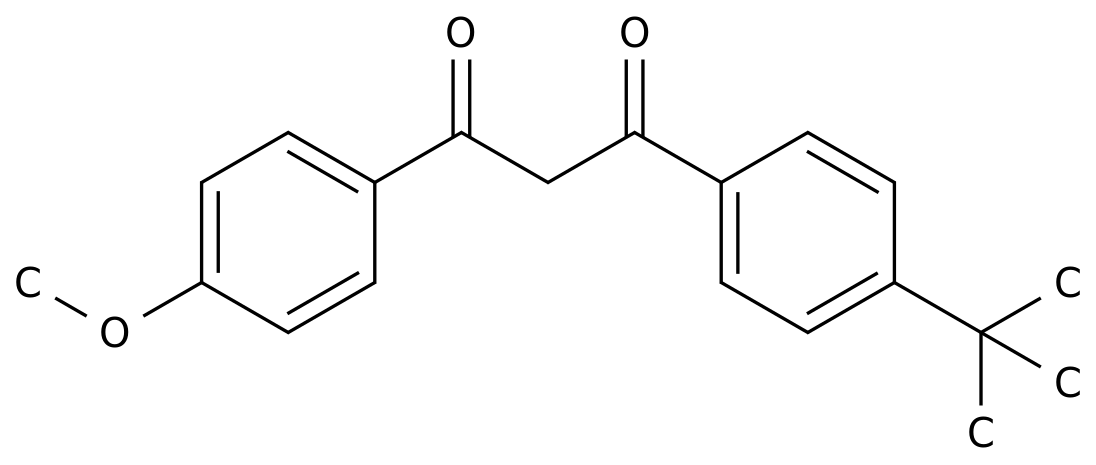
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Whether bullish or bearish on oil, gas or renewables, there is little controversy
in the conclusions when it comes to the main growth points of the energy sector in 2019.
Over the past three years, the global growth of carbon-centric energy has been relatively high, as well as the development of renewable energy has accelerated
significantly.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), spending on renewables continues to outpace fossil fuel-based electricity
.
The United Nations predicts that the world's population will grow from 7.
6 billion to 9.
8 billion by 2050, which, combined with rapid urbanization, will continue to drive energy demand
.
Global electricity demand is growing about twice as fast as overall energy use and could grow by more than 50% by 2040, with energy demand increasing by 25%.
At the same time, the challenge of meeting growing energy demand while reducing harmful emissions and greenhouse gases remains a very important challenge
.
In 2017, the global atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide rose by 1.
4%, the largest annual increase
on record.
Growth Point 1: Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector has been growing continuously over the past few years and is likely to remain that way
for years to come.
According to the IEA's 2019 Renewable Energy Report, renewable energy is sweeping the globe and penetrating the global energy system
at an unprecedented rate.
According to the Solar Energy Industry Association (SEIA), the United States installed 4.
8 GW of solar photovoltaic capacity in the first half of 2019, up 2.
1%
year-on-year.
About 38% of new energy comes from solar energy, making it the country's second largest source
of new energy after natural gas.
Globally, PV installations are expected to reach a new high of 114.
5 GW, up 17.
5%
year-on-year.
Wind power remains an underutilized energy source, accounting for only 0.
3% of the world's
energy demand.
However, with the IEA predicting that offshore wind will become a $1 trillion industry by 2040, the industry is on the cusp of incredible growth
.
After a brief slowdown in 2018, wind energy began to rebound
in 2019.
The American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) said 1,927 MW of wind installations were completed in the third quarter, bringing the country's total installed capacity to 100GW, and total installations are expected to grow nearly 8%
year-on-year.
Overall, the outlook for global renewables is indeed bright, with the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicting that the sector will grow by 50% between 2019 and 2024 to 3,700GW.
In 2017, renewables met 8.
5% of global energy needs, but by 2040, that figure could reach nearly 30%.
Growth Point 2: Natural Gas
Natural gas demand grew at an incredible 4.
6% growth rate in 2018, with deliveries of 314 million tonnes, and the growth trend has continued into this year, driven by factors such as the global energy transition from coal-fired electricity, moderate economic growth, and falling costs
.
Natural gas now accounts for 45%
of the increase in energy consumption.
Gas demand is expected to slow down, with demand growing by 2 percent in 2019 and an average of 1.
6 percent per year over the next five years, largely due to declining consumption in China, which is expected to grow just 8 percent
annually through 2024, the IEA said.
The IEA expects natural gas consumption to grow by 40% to nearly 200 trillion Btu
by 2050.
Natural gas can play a key role
in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The rapid spread of natural gas is responsible for
the continued decline in coal-fired power generation in many countries, including the United States.
Growth Point 3: Nuclear Power
Nuclear power continues to make an increasing contribution
to the search for clean and reliable energy sources.
In 2019, the global nuclear power generation was 2,563 TWh from the 449 reactors that are operational around the world, of which 9 new reactors were connected to the grid and 7 were closed
.
Currently, a total of 55 reactors are under construction, of which 5 have started construction
.
The sector is experiencing strong growth, with more than 20 new reactors planned to be connected to the grid by
the end of 2020.
At present, nuclear energy provides about 10% of the world's electricity, making it the world's second largest low-carbon energy source
.
This proportion is expected to remain constant
until 2050.
Despite much controversy over nuclear power, this trend is expected to continue
for decades to come.
Energy base: oil
Compared to last year's peak, oil field pumping volume around the world has been greatly reduced
this year.
According to Y-Charts, crude oil production was 82.
46 million bpd in August, compared to 84.
72 million b/d in November 2018, the highest level
in five years.
However, the decline was mainly from OPEC producers, with the United States producing a record 12.
8 million b/d, the highest
of any country.
But while we want to rapidly increase the use of renewable and clean energy, we can't keep up with growing energy demand
fast enough.
Therefore, oil production is expected to continue to grow in the next decade, of which the United States accounts for 85%.
Lost coal
In the global energy transition, coal is becoming the biggest loser
.
According to CarbonBrief, global coal-fired power generation is expected to decline by 300 TWh, or 3 percent
, this year.
The largest uses of coal are power generation, cement manufacturing, steel production, and use as a liquid fuel
.
In developed countries, including the European Union, Germany and South Korea, coal power generation is showing a record downward trend, while growth in other countries cannot be
matched.
The largest decrease was in the United States, where several large coal-fired power plants recently closed
.
Currently, about 38% of the world's electricity comes from coal-fired power plants, 13 percentage points
higher than the second-ranked renewables.
The main force of this growth trend is the increase
in power generation in Southeast Asia.
But with calls to phase out global coal, coal power generation could fall below 30 percent in less than two decades, with renewables becoming the main source
of electricity.
Whether bullish or bearish on oil, gas or renewables, there is little controversy
in the conclusions when it comes to the main growth points of the energy sector in 2019.
Over the past three years, the global growth of carbon-centric energy has been relatively high, as well as the development of renewable energy has accelerated
significantly.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), spending on renewables continues to outpace fossil fuel-based electricity
.
The United Nations predicts that the world's population will grow from 7.
6 billion to 9.
8 billion by 2050, which, combined with rapid urbanization, will continue to drive energy demand
.
Global electricity demand is growing about twice as fast as overall energy use and could grow by more than 50% by 2040, with energy demand increasing by 25%.
At the same time, the challenge of meeting growing energy demand while reducing harmful emissions and greenhouse gases remains a very important challenge
.
In 2017, the global atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide rose by 1.
4%, the largest annual increase
on record.
Growth Point 1: Renewable Energy
Growth Point 1: Renewable EnergyThe renewable energy sector has been growing continuously over the past few years and is likely to remain that way
for years to come.
According to the IEA's 2019 Renewable Energy Report, renewable energy is sweeping the globe and penetrating the global energy system
at an unprecedented rate.
According to the Solar Energy Industry Association (SEIA), the United States installed 4.
8 GW of solar photovoltaic capacity in the first half of 2019, up 2.
1%
year-on-year.
About 38% of new energy comes from solar energy, making it the country's second largest source
of new energy after natural gas.
Globally, PV installations are expected to reach a new high of 114.
5 GW, up 17.
5%
year-on-year.
Wind power remains an underutilized energy source, accounting for only 0.
3% of the world's
energy demand.
However, with the IEA predicting that offshore wind will become a $1 trillion industry by 2040, the industry is on the cusp of incredible growth
.
After a brief slowdown in 2018, wind energy began to rebound
in 2019.
The American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) said 1,927 MW of wind installations were completed in the third quarter, bringing the country's total installed capacity to 100GW, and total installations are expected to grow nearly 8%
year-on-year.
Overall, the outlook for global renewables is indeed bright, with the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicting that the sector will grow by 50% between 2019 and 2024 to 3,700GW.
In 2017, renewables met 8.
5% of global energy needs, but by 2040, that figure could reach nearly 30%.
Growth Point 2: Natural Gas
Growth Point 2: Natural GasNatural gas demand grew at an incredible 4.
6% growth rate in 2018, with deliveries of 314 million tonnes, and the growth trend has continued into this year, driven by factors such as the global energy transition from coal-fired electricity, moderate economic growth, and falling costs
.
Natural gas now accounts for 45%
of the increase in energy consumption.
Gas demand is expected to slow down, with demand growing by 2 percent in 2019 and an average of 1.
6 percent per year over the next five years, largely due to declining consumption in China, which is expected to grow just 8 percent
annually through 2024, the IEA said.
The IEA expects natural gas consumption to grow by 40% to nearly 200 trillion Btu
by 2050.
Natural gas can play a key role
in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The rapid spread of natural gas is responsible for
the continued decline in coal-fired power generation in many countries, including the United States.
Growth Point 3: Nuclear Power
Growth Point 3: Nuclear PowerNuclear power continues to make an increasing contribution
to the search for clean and reliable energy sources.
In 2019, the global nuclear power generation was 2,563 TWh from the 449 reactors that are operational around the world, of which 9 new reactors were connected to the grid and 7 were closed
.
Currently, a total of 55 reactors are under construction, of which 5 have started construction
.
The sector is experiencing strong growth, with more than 20 new reactors planned to be connected to the grid by
the end of 2020.
At present, nuclear energy provides about 10% of the world's electricity, making it the world's second largest low-carbon energy source
.
This proportion is expected to remain constant
until 2050.
Despite much controversy over nuclear power, this trend is expected to continue
for decades to come.
Energy base: oil
Energy base: oilCompared to last year's peak, oil field pumping volume around the world has been greatly reduced
this year.
According to Y-Charts, crude oil production was 82.
46 million bpd in August, compared to 84.
72 million b/d in November 2018, the highest level
in five years.
However, the decline was mainly from OPEC producers, with the United States producing a record 12.
8 million b/d, the highest
of any country.
But while we want to rapidly increase the use of renewable and clean energy, we can't keep up with growing energy demand
fast enough.
Therefore, oil production is expected to continue to grow in the next decade, of which the United States accounts for 85%.
Lost coal
Lost coalIn the global energy transition, coal is becoming the biggest loser
.
According to CarbonBrief, global coal-fired power generation is expected to decline by 300 TWh, or 3 percent
, this year.
The largest uses of coal are power generation, cement manufacturing, steel production, and use as a liquid fuel
.
In developed countries, including the European Union, Germany and South Korea, coal power generation is showing a record downward trend, while growth in other countries cannot be
matched.
The largest decrease was in the United States, where several large coal-fired power plants recently closed
.
Currently, about 38% of the world's electricity comes from coal-fired power plants, 13 percentage points
higher than the second-ranked renewables.
The main force of this growth trend is the increase
in power generation in Southeast Asia.
But with calls to phase out global coal, coal power generation could fall below 30 percent in less than two decades, with renewables becoming the main source
of electricity.