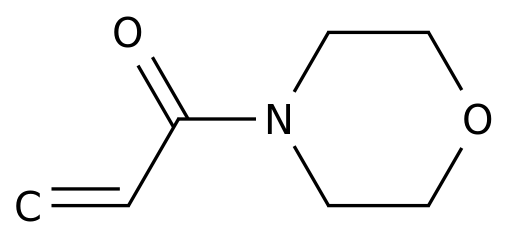
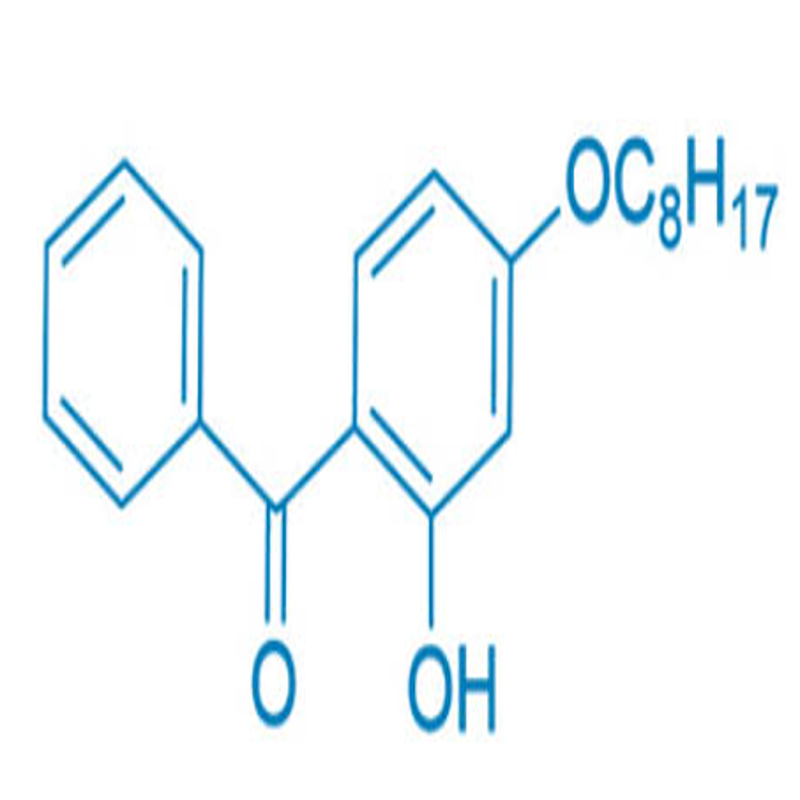
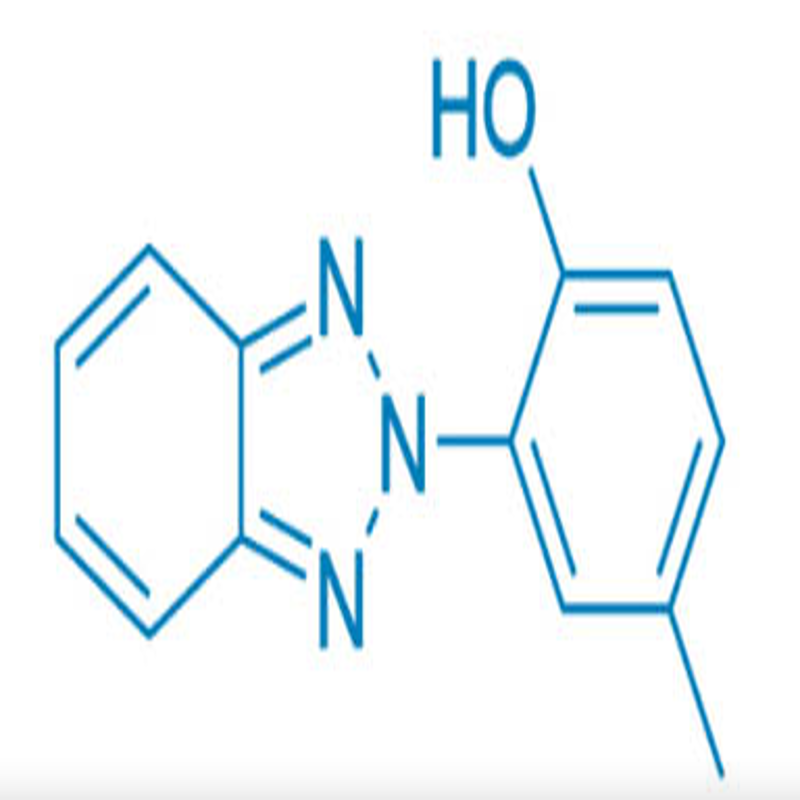
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
A team of researchers in the United States has shown that the performance of lithium-ion batteries can be optimized
by using a lower proportion of lithium and other metals.
The performance of lithium-ion batteries is expected to be optimized by reducing the proportion of lithium
An international team led by researchers at the U.
S.
Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory used advanced electron microscopy techniques to show how the different components of the cathode material affect the structure of the battery at the yard level, and how it works
efficiently.
Lithium-ion batteries are used in energy storage units
in electronics, electric vehicles and power grids.
The new study aims to overcome some drawbacks, such as limited number of charges and reduced capacity during the service life
.
Alpesh Khushalchand Shukla, a scientist at Berkeley Lab's Institute for Molecular Casting, said: "This discovery may change the way we study phase transitions within cathodes and the resulting loss of capacity in materials
.
”
,
A team of researchers in the United States has shown that the performance of lithium-ion batteries can be optimized
by using a lower proportion of lithium and other metals.
The performance of lithium-ion batteries is expected to be optimized by reducing the proportion of lithium
The performance of lithium-ion batteries is expected to be optimized by reducing the proportion of lithiumAn international team led by researchers at the U.
S.
Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory used advanced electron microscopy techniques to show how the different components of the cathode material affect the structure of the battery at the yard level, and how it works
efficiently.
Lithium-ion batteries are used in energy storage units
in electronics, electric vehicles and power grids.
The new study aims to overcome some drawbacks, such as limited number of charges and reduced capacity during the service life
.
Alpesh Khushalchand Shukla, a scientist at Berkeley Lab's Institute for Molecular Casting, said: "This discovery may change the way we study phase transitions within cathodes and the resulting loss of capacity in materials
.
”
,