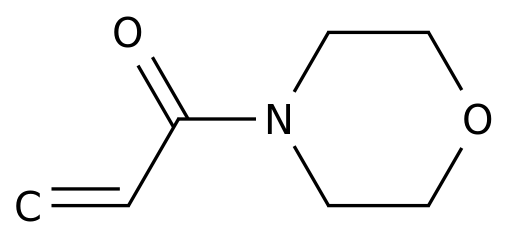
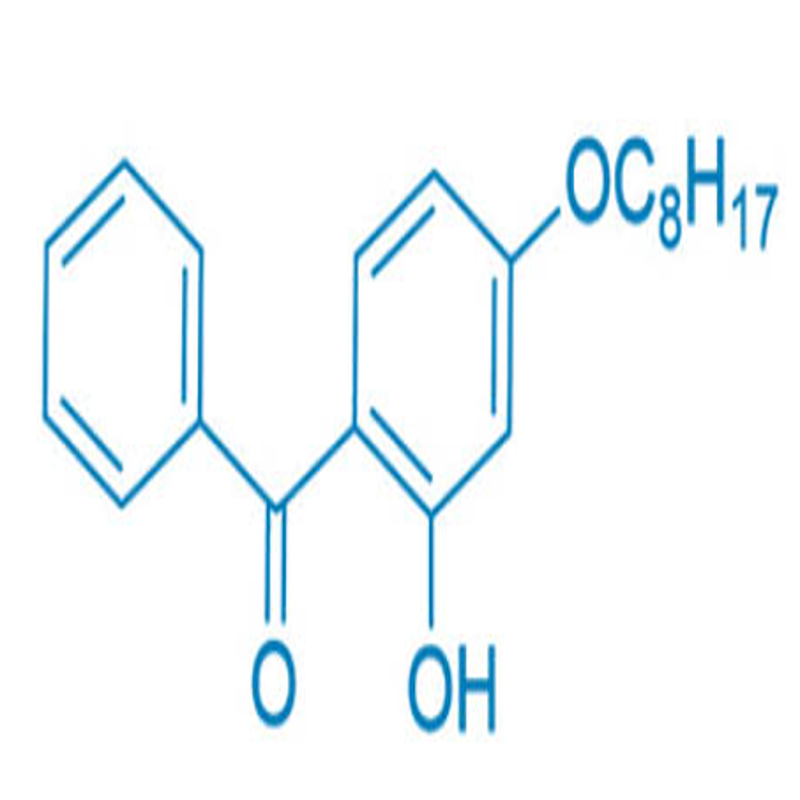
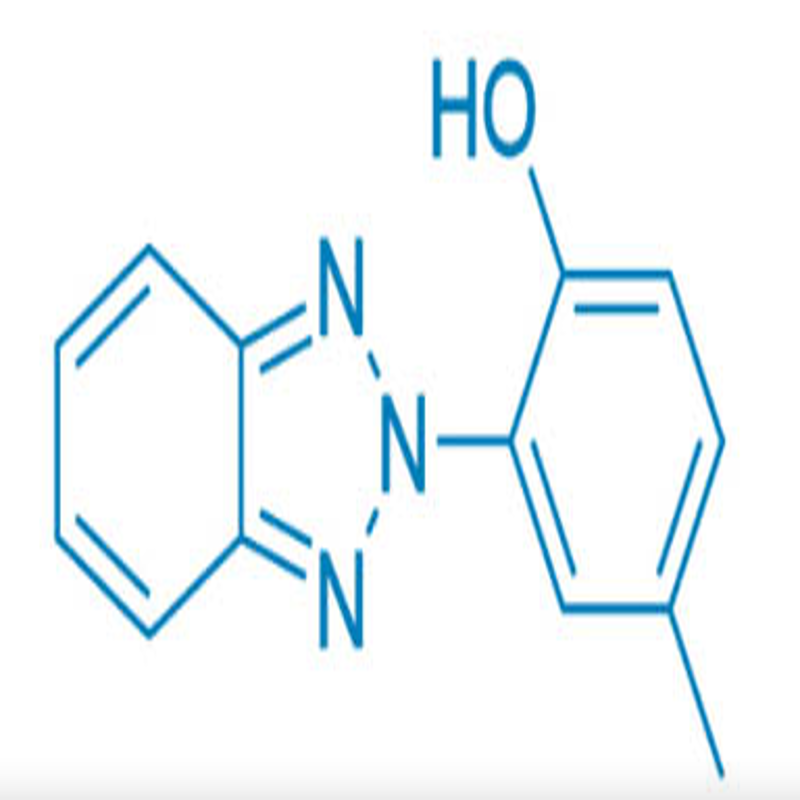
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
In the third quarter of 2018, utility-scale solar installations in the U.
S.
fell below
1 GW for the first time since 2015 due to delays caused by Section 201 solar tax rate issues.
In the latest U.
S.
Solar Market Report, Wood Mackenzie Power & Renewables and the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) forecast a rebound in the fourth quarter, with an additional 3.
5 GW of utility-scale photovoltaic (PV) capacity, expected to be the largest installation in a single quarter since late 2016
.
The weak third-quarter data reflects uncertainty over the implementation of solar tariffs in late 2017 and early 2018, which led to project delays
.
"However, we did see utility PV purchases well over installations in the third quarter, suggesting that despite project delays caused by tax rate issues, there is still room for significant growth in the U.
S.
utility PV industry," said
Colin Smith, senior analyst at Wood Mackenzie.
Wood Mackenzie Market Research and SEIA have observed a surge in utility-scale solar purchases, with 11.
2 GW of direct current (DC) projects
announced so far in 2018.
In the third quarter, the U.
S.
solar market grew 1.
7 gigawatts (DC), down 15% year-over-year and up 20%
sequentially.
This is primarily due to a decline
in utility-scale capacity.
Residential solar installations were largely flat, with non-residential PV installations up 6% in the quarter but down 6%
year-on-year.
Wood Mackenzie now forecasts total PV installations in the US for 2018 at 11.
1 GW
.
In the third quarter of 2018, utility-scale solar installations in the U.
S.
fell below
1 GW for the first time since 2015 due to delays caused by Section 201 solar tax rate issues.
In the latest U.
S.
Solar Market Report, Wood Mackenzie Power & Renewables and the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) forecast a rebound in the fourth quarter, with an additional 3.
5 GW of utility-scale photovoltaic (PV) capacity, expected to be the largest installation in a single quarter since late 2016
.
The weak third-quarter data reflects uncertainty over the implementation of solar tariffs in late 2017 and early 2018, which led to project delays
.
"However, we did see utility PV purchases well over installations in the third quarter, suggesting that despite project delays caused by tax rate issues, there is still room for significant growth in the U.
S.
utility PV industry," said
Colin Smith, senior analyst at Wood Mackenzie.
Wood Mackenzie Market Research and SEIA have observed a surge in utility-scale solar purchases, with 11.
2 GW of direct current (DC) projects
announced so far in 2018.
In the third quarter, the U.
S.
solar market grew 1.
7 gigawatts (DC), down 15% year-over-year and up 20%
sequentially.
This is primarily due to a decline
in utility-scale capacity.
Residential solar installations were largely flat, with non-residential PV installations up 6% in the quarter but down 6%
year-on-year.
Wood Mackenzie now forecasts total PV installations in the US for 2018 at 11.
1 GW
.