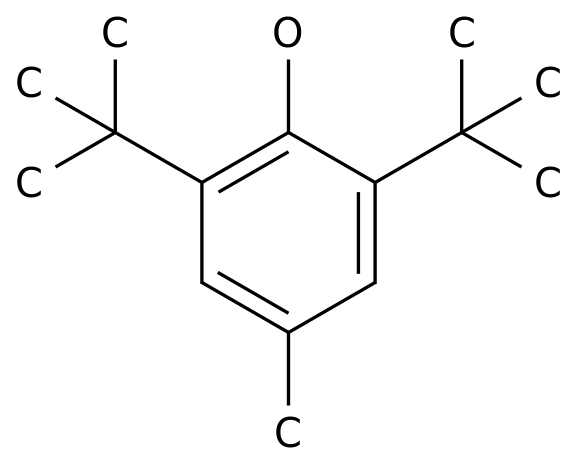
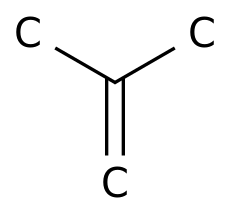
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Introduction
IntroductionIn response to the special national conditions of lack of natural resources, the Swiss federal government has paid great attention to the development of circular economy as early as the middle of the last century
.
With the goal of realizing the development model of waste reduction, recycling and harmlessness, the Swiss government has always been committed to the development of the resource recycling industry in the entire process of investment, production, consumption and waste disposal
.
After decades of hard work, Switzerland, a country with an area of only 41,000 square kilometers and a population of just over 7 million, ranks first in the world with an annual per capita income of more than 45,700 US dollars and ranks first among countries with a population of more than one million.
It is also a world leader in environmental protection
.
Find the right model according to local conditions
Find the right model according to local conditionsThe whole of Switzerland is located in the Alps, known as the "Roof of the World".
More than 60% of the country is located between high mountains and mountains with an average altitude of 3,000-4,000 meters.
snow mountain
.
The severe cold of the long winter and the vertically distributed mountain climate restrict the development of agriculture and animal husbandry; Switzerland's mineral resources are also extremely poor, and almost all metal raw materials must be imported.
Such objective conditions seriously restrict the development of Switzerland's domestic industrial production
.
The harsh natural environment forces Switzerland to find an economic development model that suits its own country
.
The Swiss federal government starts with advocating resource conservation, protecting the environment, and encouraging investment in recycling industries, giving priority to the development of the tertiary industry, focusing on the protection of intangible assets, and vigorously developing the financial industry
.
After decades of national efforts, tourism has now become one of the pillar industries of the Swiss national economy
.
According to the data released by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office, in 2003, the tourism industry generated 22.
2 billion Swiss francs (about 144.
5 billion yuan), accounting for 5.
2% of the GDP of that year; in 2004, the number of overnight tourists in Switzerland increased by 1.
7% over the previous year; Swiss tourism The bureau said that in 2005 the number of tourists to Switzerland will increase by 2.
7% compared to the previous year
.
Switzerland pays attention to the development of independent intellectual property rights, and has many world-renowned brand products, such as Swiss watches, Nescafé coffee, textile machinery, ABB complete sets of electrical equipment, Novartis and Roche's many inventions in the field of medicine, etc.
, which have attracted wide attention and are very popular in many countries.
.
Switzerland's well-developed banking industry attracts more than 4.
2 trillion Swiss francs of funds from around the world
.
Recycling turns waste into treasure
Recycling turns waste into treasureIn the whole of Europe, Switzerland was the first to recycle plastic products
.
Since plastic products have generally entered Swiss households, recycling this renewable resource has become a concern of the entire Swiss society
.
To this end, the federal government has also taken a series of supporting measures
.
Taking the recycling of waste plastic bottles as an example, there are currently more than 15,000 waste plastic bottle recycling centers in Switzerland, and more than 100 plastic bottles are sent to recycling centers per capita every year; the national recycling rate of waste plastic bottles has exceeded 80%.
, while the recovery rate in other European countries is only hovering between 20%-40%
.
In an interview with the Swiss Federal Energy Agency, the reporter learned that the main reason why Switzerland can achieve such a high recycling rate is that the government expressly stipulates that relevant enterprises across the country can only recycle their plastic bottles after reaching a recycling rate of more than 75%.
Eligible to continue producing or using plastic bottles as packaging
.
At present, there are 5 large-scale plastic recycling, sorting and processing centers in Switzerland.
Among them, the new processing center in Vaud can handle 150,000 plastic bottles per hour, and classify and process plastics of various colors into new plastic materials.
.
In addition to plastic products, discarded cans, all kinds of old batteries, and even mobile phones are all objects of recycling
.
At present, there are more than 4,000 waste cans recycling bins in Switzerland, with an annual recycling volume of about 12,000-14,000 tons, and the annual recycling volume of each citizen is about 2 kg
.
The technology for recycling and reusing old batteries is complex and expensive
.
It is reported that there are only two large used battery recycling and processing companies in the world, and one of them is located in Switzerland
.
Relevant Swiss regulations stipulate that residents are not allowed to discard ordinary old batteries, let alone car batteries, and batteries cannot be mixed with other garbage for disposal
.
According to the data of the Swiss Federal Statistical Office, the recycling rate of used batteries in Switzerland has reached more than 65%, and the government expects it to reach more than 80%
.
The recycling of old mobile phones is a new project.
In view of the fact that more than 1.
5 million mobile phones are replaced and discarded every year among the population of more than 7 million in Switzerland, the Swiss federal government established a special agency in 2003 and carried out every Pay 5-10 CHF for recycling of old mobile phones
.
The recovered and intact old mobile phones are concentrated in a special factory outside Geneva for testing, sorting, dismantling and other processing procedures, and the available parts are taken out for reassembly
.
For scrapped old mobile phones, they are used for recycling after scientific treatment
.
Circular economy legislation first
Circular economy legislation firstSwitzerland has many successful experiences in the recycling and utilization of renewable resources.
In addition to following the internationally accepted 4Rs (Reduce-reduction, Recover-regeneration, Reuse-reuse, Recycle-recycling) principles of circular economy, the Swiss government also Encouraging national recycling of renewable resources through legislation
.
The Swiss federal government has successively formulated a series of laws and regulations to regulate the specific work of developing a circular economy, including the "Regulations on the Advance Collection of Glass Beverage Packaging Disposal Fees", "Battery Disposal Fee Standards", and "Regulations on the Recycling of Electronic and Electrical Products" , "Special Garbage Recycling and Transportation Regulations", "Water Resources Protection Law", "Environmental Protection Law", "Water Resources from Pollution and Air Cleaning Law" and dozens of other laws and regulations
.
In addition, there are many private "recycling associations" dedicated to the recycling of renewable resources in Switzerland, and a network is formed to strengthen the links between various recycling organizations and disseminate the latest information on the classification, recycling, processing and processing of renewable resources
.
Such associations have become an important organization in the Swiss recycling system due to their independence and professionalism, and play a role in closely connecting official institutions, retailers, and even ordinary residents
.