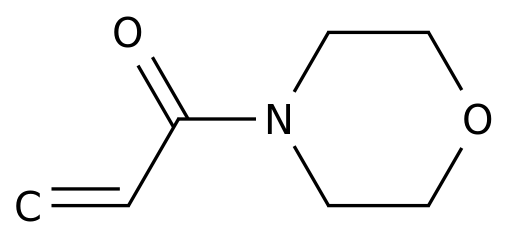
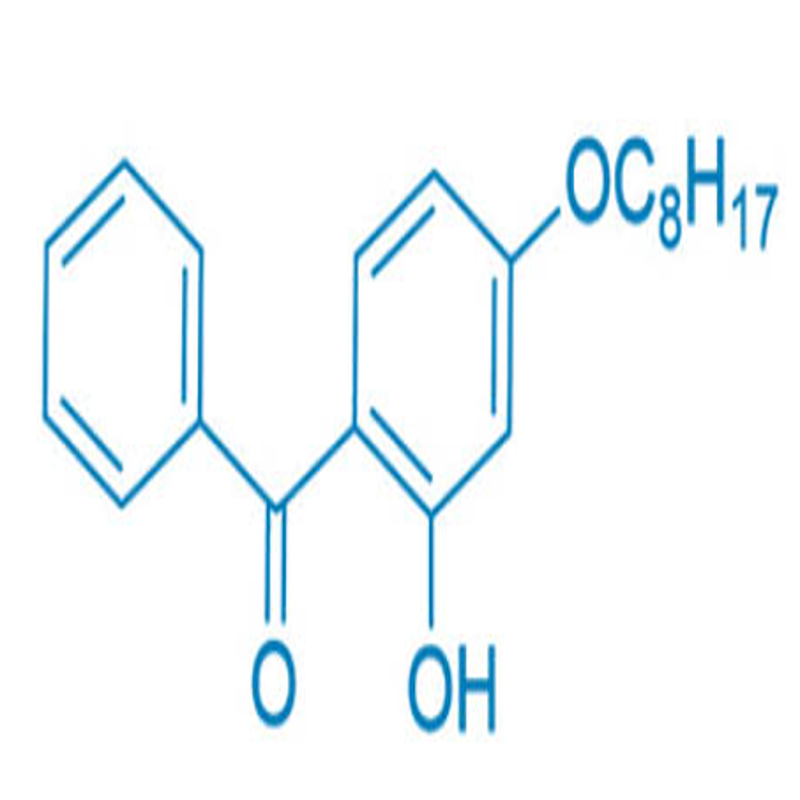
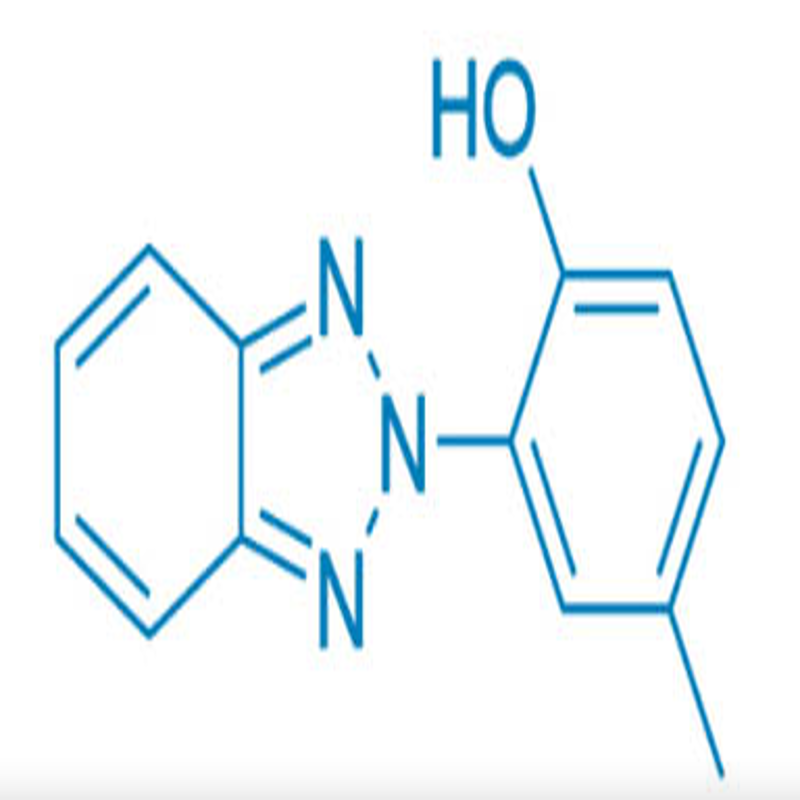
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
In recent years, Japan has begun to return to coal-fired and thermal power generation, according to statistics, in the past two years, Japan has opened more than 8 coal-fired power plants, and plans to add 36 new thermal power plants
in 10 years.
Japan will also update its energy plan, in which coal-fired power generation will provide 26% of Japan's electricity by 2030, abandoning the previous target
of reducing to 10%.
According to analysis, one of the reasons for the big turn of the energy blueprint is the Fukushima nuclear energy incident in 2011, when the impact of the nuclear disaster affected the Japanese public's support for nuclear energy, and Japan's 54 nuclear reactors were completely shut down, and only 7 nuclear reactors have been reopened
.
However, there are also critics who point out that Japan has not strongly supported renewable energy investment, and if coal-fired power generation returns in the future, it will greatly affect air quality and emission reduction targets
.
In recent years, Japan has begun to return to coal-fired and thermal power generation, according to statistics, in the past two years, Japan has opened more than 8 coal-fired power plants, and plans to add 36 new thermal power plants
in 10 years.
Japan will also update its energy plan, in which coal-fired power generation will provide 26% of Japan's electricity by 2030, abandoning the previous target
of reducing to 10%.
According to analysis, one of the reasons for the big turn of the energy blueprint is the Fukushima nuclear energy incident in 2011, when the impact of the nuclear disaster affected the Japanese public's support for nuclear energy, and Japan's 54 nuclear reactors were completely shut down, and only 7 nuclear reactors have been reopened
.
However, there are also critics who point out that Japan has not strongly supported renewable energy investment, and if coal-fired power generation returns in the future, it will greatly affect air quality and emission reduction targets
.