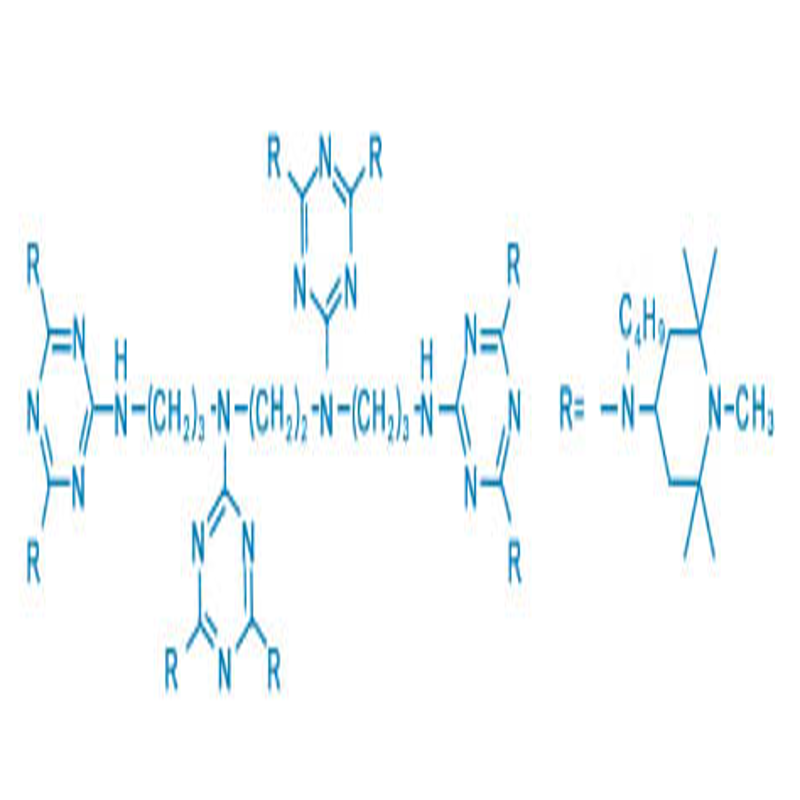
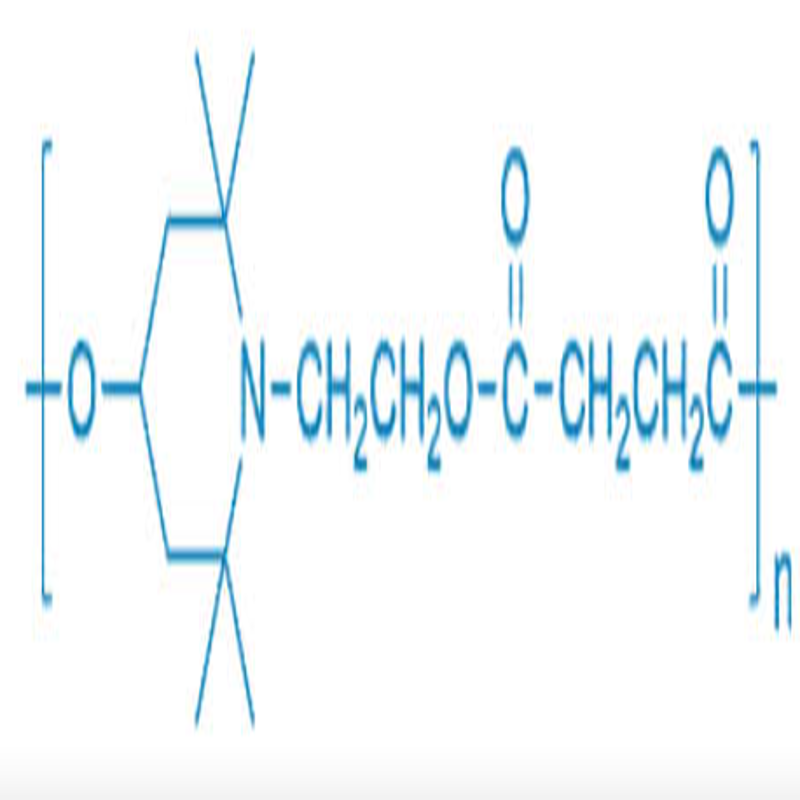
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Wood Mackenzie said investment in renewable energy generation in the Asia-Pacific region could double from the previous decade to $1.
3 trillion by 2030, bringing fossil fuel electricity spending down by about 25 percent annually to $54 billion
.
Alex Whitworth, head of research at the consultancy, said: "Asia Pacific is a world leader in power generation investment, expected to reach $2.
4 trillion within a decade, with renewables accounting for more than half of electricity investment.
.
.
"
Woodmac said in a report on Tuesday that Chinese mainland, Japan, India, South Korea and Taiwan will be the largest contributors to renewable energy investment, including solar and wind, with an average of about 140 GW of new capacity added annually
.
In contrast, Mr Wood Mackenzie said renewable investment in Australia – a leader in the Asia-Pacific region's energy transition – would fall by 60 per cent over the next five years, but pick up again in the 30s to an average of $
7 billion a year.
"The country is shutting down aging coal-fired power plants and is facing reliability and cost challenges
at least 10 years ahead of other Asian countries.
" Whitworth said coal is expected to account for 55 percent of fossil fuel investment in the Asia-Pacific region by 2030, before shrinking to 30 percent
in the 30s due to natural gas dominance.
By 2025, carbon emissions from the region's power sector could peak
at 7.
3 billion tonnes.
Whitworth said that while carbon emissions from the region's power sector are expected to fall by 47% from their 2025 peak, "the inertia of coal power facilities will hinder the Asia-Pacific region from achieving carbon-free electricity by 2050.
"
Whitworth said new technologies such as carbon capture and storage and green fuels including hydrogen, ammonia and biomass will be key
to reducing emissions from the power sector.
Wood Mackenzie said investment in renewable energy generation in the Asia-Pacific region could double from the previous decade to $1.
3 trillion by 2030, bringing fossil fuel electricity spending down by about 25 percent annually to $54 billion
.
Alex Whitworth, head of research at the consultancy, said: "Asia Pacific is a world leader in power generation investment, expected to reach $2.
4 trillion within a decade, with renewables accounting for more than half of electricity investment.
.
.
"
Woodmac said in a report on Tuesday that Chinese mainland, Japan, India, South Korea and Taiwan will be the largest contributors to renewable energy investment, including solar and wind, with an average of about 140 GW of new capacity added annually
.
In contrast, Mr Wood Mackenzie said renewable investment in Australia – a leader in the Asia-Pacific region's energy transition – would fall by 60 per cent over the next five years, but pick up again in the 30s to an average of $
7 billion a year.
"The country is shutting down aging coal-fired power plants and is facing reliability and cost challenges
at least 10 years ahead of other Asian countries.
" Whitworth said coal is expected to account for 55 percent of fossil fuel investment in the Asia-Pacific region by 2030, before shrinking to 30 percent
in the 30s due to natural gas dominance.
By 2025, carbon emissions from the region's power sector could peak
at 7.
3 billion tonnes.
Whitworth said that while carbon emissions from the region's power sector are expected to fall by 47% from their 2025 peak, "the inertia of coal power facilities will hinder the Asia-Pacific region from achieving carbon-free electricity by 2050.
"
Whitworth said new technologies such as carbon capture and storage and green fuels including hydrogen, ammonia and biomass will be key
to reducing emissions from the power sector.