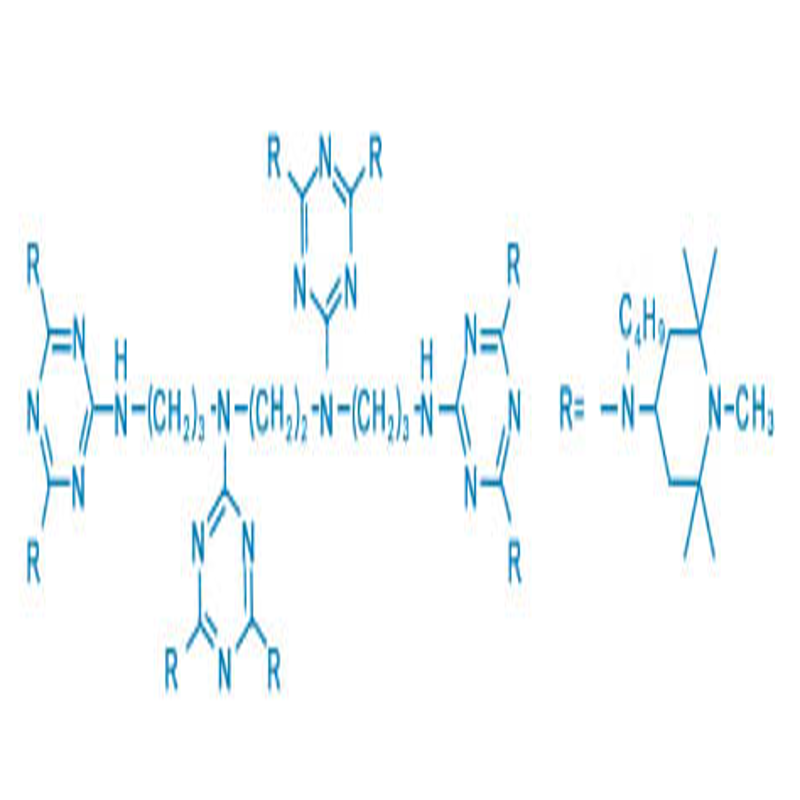
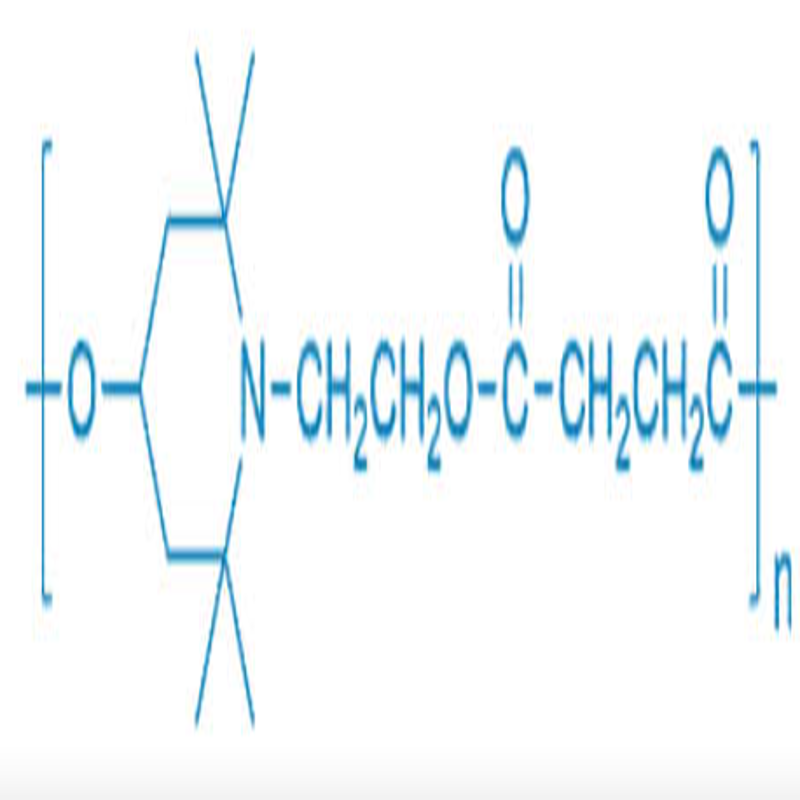
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to the latest report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), after the biggest decline in decades, global electricity demand will rebound
modestly in 2021, led by growth in China, India and other emerging economies.
According to the IEA's first Electricity Market Report, the historic shock of the Covid-19 crisis will lead to a 2%
drop in global electricity demand in 2020.
As the world economy recovers in 2021, electricity demand is expected to grow by around 3%, although this is significantly lower than the
demand rebound of more than 7% in 2010 after the global financial crisis.
In 2020, China will be the only major economy
with positive electricity demand growth.
However, its expected growth is about 2%, well below its recent average of 6.
5%.
Other big electricity consumers, including the United States, India, Europe, Japan, South Korea and Southeast Asia, will experience declines
throughout the year.
Renewable energy generation is expected to compress traditional energy sources by nearly 7% by 2020, such as hydroelectric, wind and solar
.
Coal-fired power generation is expected to fall by about 5 percent, the largest decline on record; Nuclear power generation about 4%; Gas-fired power generation increased by 2%.
Overall, CO2 emissions from power generation are expected to fall by 5%
by 2020.
Dr Fatih Birol, Executive Director of the IEA, said: "Electricity plays a central role in today's energy world and will become increasingly important as the transition to clean energy accelerates
.
”
Falling demand, lower fuel prices and an increase in renewable energy generation dragged down wholesale electricity prices
in 2020.
The IEA's wholesale electricity market price index, which tracks price movements in major advanced economies, shows that the average price of electricity has fallen by 28% this year, after a 12%
decline in 2019.
Renewable energy generation is expected to continue to grow in 2021 by more than 6%, expanding the share of renewables in the electricity mix from 28% in 2020 to 29%.
With the rebound in France and Japan, and the coming online of new nuclear power plants in China and the UAE, nuclear power will grow by 2.
5%
next year.
The net result of global expectations is that coal-fired power generation will grow by about 3% by 2021, while that of gas-fired power plants by about 1%.
This will lead to an increase in CO2 emissions from the power sector by around 2%
in 2021.
According to the latest report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), after the biggest decline in decades, global electricity demand will rebound
modestly in 2021, led by growth in China, India and other emerging economies.
According to the IEA's first Electricity Market Report, the historic shock of the Covid-19 crisis will lead to a 2%
drop in global electricity demand in 2020.
As the world economy recovers in 2021, electricity demand is expected to grow by around 3%, although this is significantly lower than the
demand rebound of more than 7% in 2010 after the global financial crisis.
In 2020, China will be the only major economy
with positive electricity demand growth.
However, its expected growth is about 2%, well below its recent average of 6.
5%.
Other big electricity consumers, including the United States, India, Europe, Japan, South Korea and Southeast Asia, will experience declines
throughout the year.
Renewable energy generation is expected to compress traditional energy sources by nearly 7% by 2020, such as hydroelectric, wind and solar
.
Coal-fired power generation is expected to fall by about 5 percent, the largest decline on record; Nuclear power generation about 4%; Gas-fired power generation increased by 2%.
Overall, CO2 emissions from power generation are expected to fall by 5%
by 2020.
Dr Fatih Birol, Executive Director of the IEA, said: "Electricity plays a central role in today's energy world and will become increasingly important as the transition to clean energy accelerates
.
”
Falling demand, lower fuel prices and an increase in renewable energy generation dragged down wholesale electricity prices
in 2020.
The IEA's wholesale electricity market price index, which tracks price movements in major advanced economies, shows that the average price of electricity has fallen by 28% this year, after a 12%
decline in 2019.
Renewable energy generation is expected to continue to grow in 2021 by more than 6%, expanding the share of renewables in the electricity mix from 28% in 2020 to 29%.
With the rebound in France and Japan, and the coming online of new nuclear power plants in China and the UAE, nuclear power will grow by 2.
5%
next year.
The net result of global expectations is that coal-fired power generation will grow by about 3% by 2021, while that of gas-fired power plants by about 1%.
This will lead to an increase in CO2 emissions from the power sector by around 2%
in 2021.