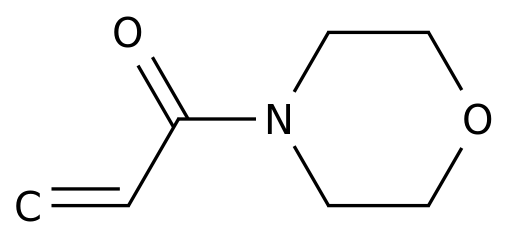
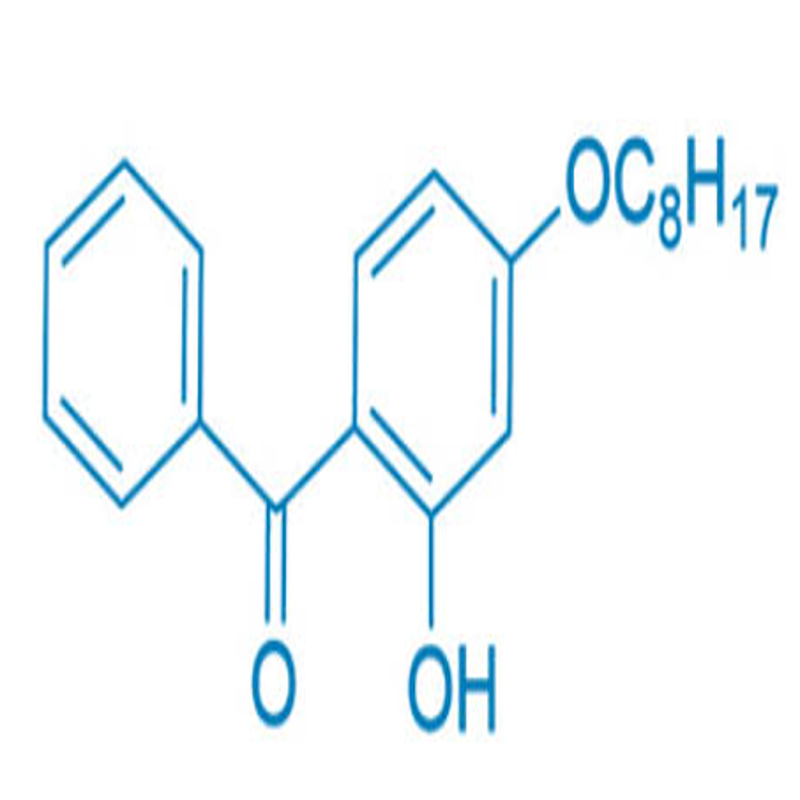
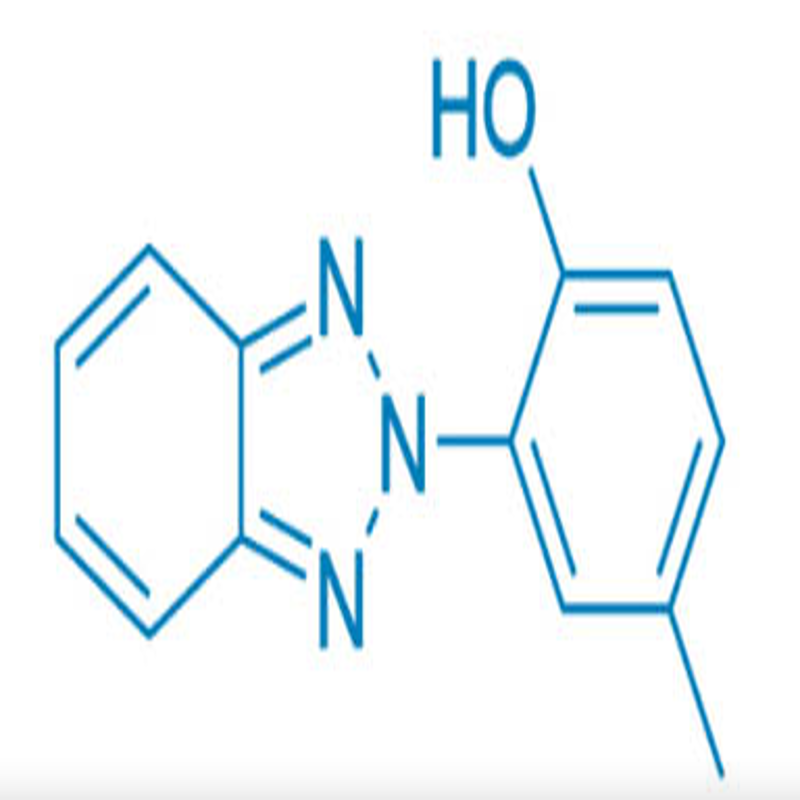
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to data from China's National Energy Administration, in the first nine months of this year, 34.
5 GW of new solar photovoltaic installed capacity was added nationwide, reaching a cumulative total of 164.
74 GW
.
Of these, about 117.
9 GW are utility-scale solar plants and 46.
8 GW are distributed generation facilities
.
Solar photovoltaic power generation projects in the first three quarters fell by 20%
compared with the same period last year.
More than half of the new commissioned capacity came from the utility-scale sector, which totaled 37, with an increase of 17.
4 GW of installed capacity year-over-year, while the distributed generation segment accounted for 17.
1 GW
.
According to Asia Clean Energy (Solar) Consulting (AECEA), China will add 30 GW to 35 GW of PV installations in 2018, down from the previous guidance
of 40 GW to 45 GW.
Other analysts, including Wood Mackenzie, GTM Research, Roth and Daiwa Capital, are forecasting between 28 GW and 35 GW
.
At the end of May this year, China's new photovoltaic policy was introduced, implementing a 10 GW cap on distributed generation and reducing the feed-in tariff subsidy policy, resulting in a decline
in overall domestic installations.
According to data from China's National Energy Administration, in the first nine months of this year, 34.
5 GW of new solar photovoltaic installed capacity was added nationwide, reaching a cumulative total of 164.
74 GW
.
Of these, about 117.
9 GW are utility-scale solar plants and 46.
8 GW are distributed generation facilities
.
Solar photovoltaic power generation projects in the first three quarters fell by 20%
compared with the same period last year.
More than half of the new commissioned capacity came from the utility-scale sector, which totaled 37, with an increase of 17.
4 GW of installed capacity year-over-year, while the distributed generation segment accounted for 17.
1 GW
.
According to Asia Clean Energy (Solar) Consulting (AECEA), China will add 30 GW to 35 GW of PV installations in 2018, down from the previous guidance
of 40 GW to 45 GW.
Other analysts, including Wood Mackenzie, GTM Research, Roth and Daiwa Capital, are forecasting between 28 GW and 35 GW
.
At the end of May this year, China's new photovoltaic policy was introduced, implementing a 10 GW cap on distributed generation and reducing the feed-in tariff subsidy policy, resulting in a decline
in overall domestic installations.