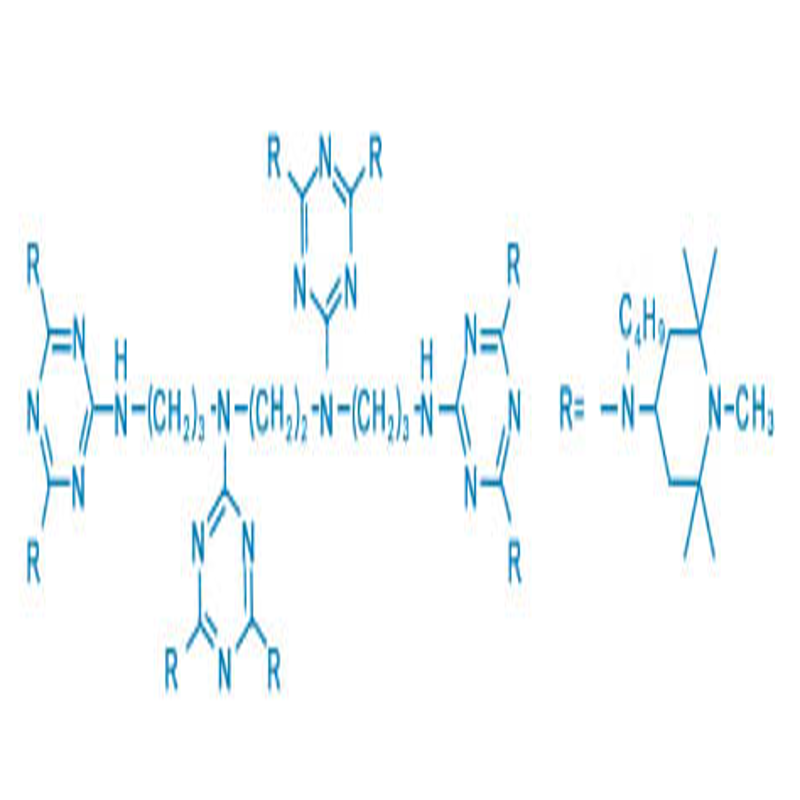
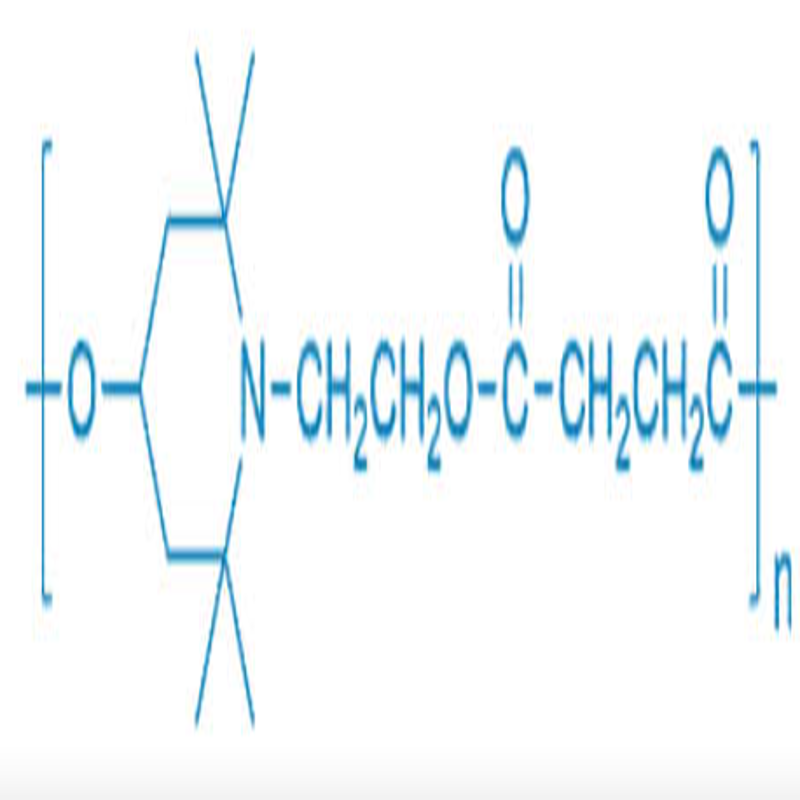
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
U.
S.
solar PV module shipments, including imports, exports, domestic production and sales, hit an all-time high of 21.
8 GW in 2020, up 5.
4 GW
from 2019.
According to the Energy Information Administration, this represents a 33%
year-on-year increase between 2019 and 2020.
Expiring solar tax credits, continued growth in utility-scale solar capacity, and falling solar system costs increased shipments
.
In 2020, 89% of U.
S.
solar PV module shipments were imported, totaling 19.
3 GW, up 26%
from 15.
3 GW imported in 2019.
Vietnam is the main importer to the United States, followed by Malaysia, South Korea and Thailand
.
Between 2019 and 2020, new installed solar PV capacity in the United States increased by 25%, utility-scale solar capacity by 29%, and small-scale solar increased by 19%.
Meanwhile, the solar investment tax credit should be reduced from 26% to 22%
in 2020.
Part of the solar capacity increase in 2020 was due to the rush to install projects
ahead of the expected ITC decline.
However, in December 2020, Congress passed an extension of the ITC to provide a 26% tax credit for solar systems installed between 2020 and 2022 and a 22% tax credit for systems installed in 2023
.
PV module costs have fallen significantly since 2010, driving solar PV module shipment growth, and lower supply chain costs and oversupply of modules due to increased production are the main reasons for
the decline in the average value of solar PV modules over the past decade.
However, due to the impact of the epidemic, the PV module supply chain was interrupted
several times in 2020.
The U.
S.
solar market has installed more than 100 GW of power generation capacity, doubling
the size of the industry in the past 3-4 years.
In 2020, the U.
S.
solar industry grew by 43%, with 19.
2 GW
installed.
According to a report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the cost of residential, commercial rooftop and utility-scale solar systems in the United States has fallen by 64 percent, 69 percent, and 82 percent
, respectively, since 2010.
The decline in the cost of residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar systems was mainly due to improved module efficiency and lower
inverter and hardware costs.
U.
S.
solar PV module shipments, including imports, exports, domestic production and sales, hit an all-time high of 21.
8 GW in 2020, up 5.
4 GW
from 2019.
According to the Energy Information Administration, this represents a 33%
year-on-year increase between 2019 and 2020.
Expiring solar tax credits, continued growth in utility-scale solar capacity, and falling solar system costs increased shipments
.
In 2020, 89% of U.
S.
solar PV module shipments were imported, totaling 19.
3 GW, up 26%
from 15.
3 GW imported in 2019.
Vietnam is the main importer to the United States, followed by Malaysia, South Korea and Thailand
.
Between 2019 and 2020, new installed solar PV capacity in the United States increased by 25%, utility-scale solar capacity by 29%, and small-scale solar increased by 19%.
Meanwhile, the solar investment tax credit should be reduced from 26% to 22%
in 2020.
Part of the solar capacity increase in 2020 was due to the rush to install projects
ahead of the expected ITC decline.
However, in December 2020, Congress passed an extension of the ITC to provide a 26% tax credit for solar systems installed between 2020 and 2022 and a 22% tax credit for systems installed in 2023
.
PV module costs have fallen significantly since 2010, driving solar PV module shipment growth, and lower supply chain costs and oversupply of modules due to increased production are the main reasons for
the decline in the average value of solar PV modules over the past decade.
However, due to the impact of the epidemic, the PV module supply chain was interrupted
several times in 2020.
The U.
S.
solar market has installed more than 100 GW of power generation capacity, doubling
the size of the industry in the past 3-4 years.
In 2020, the U.
S.
solar industry grew by 43%, with 19.
2 GW
installed.
According to a report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the cost of residential, commercial rooftop and utility-scale solar systems in the United States has fallen by 64 percent, 69 percent, and 82 percent
, respectively, since 2010.
The decline in the cost of residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar systems was mainly due to improved module efficiency and lower
inverter and hardware costs.