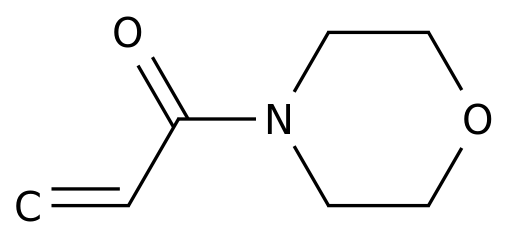
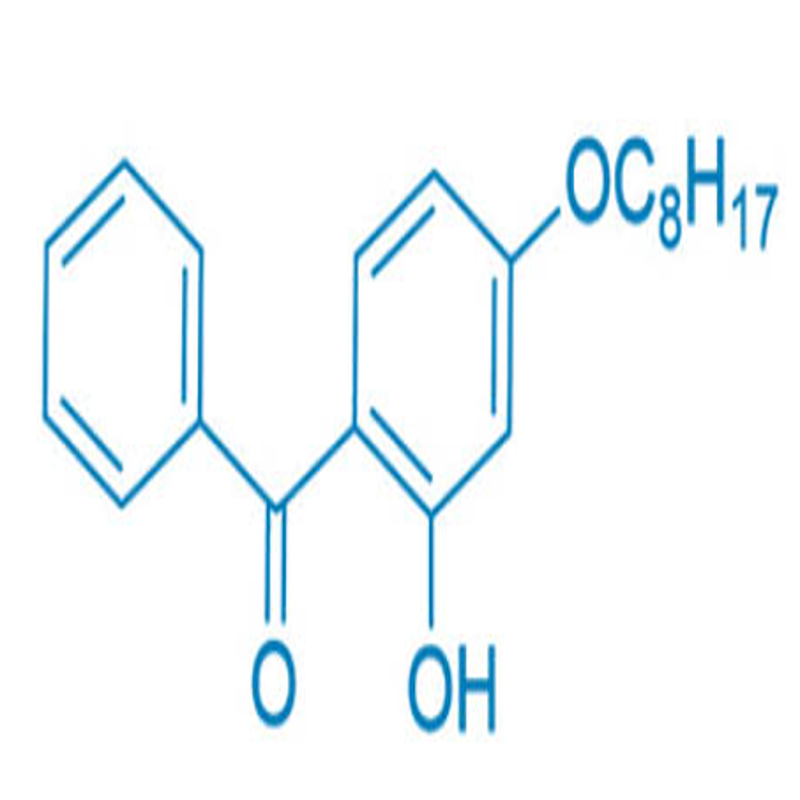
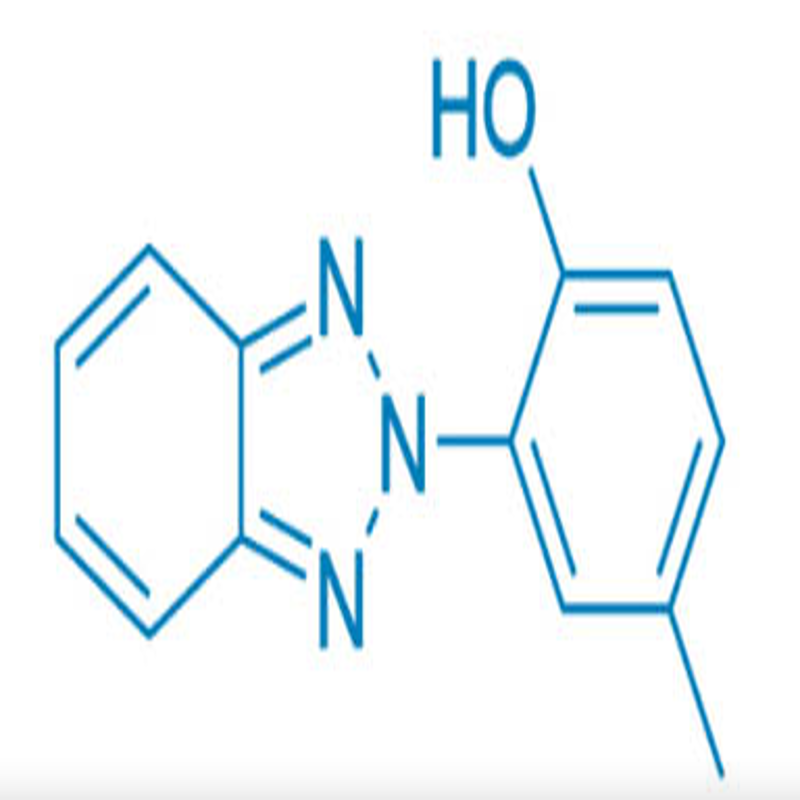
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration EIA's short-term energy outlook, SETO said that in 2019, U.
S.
wind power is expected to surpass hydropower for the first time and account for a larger proportion
of the domestic electricity mix.
Specifically, U.
S.
wind capacity is expected to increase from 96 GW at the end of 2018 to 107 GW by the end of 2019 and 114 GW by 2020, which means that 11 GW of new U.
S.
wind power will be added in 2019 and 7 GW
by 2020.
Notably, the Production Tax Credit (PTC) in the United States will have an impact
on the country's wind industry for years to come.
"The construction of new wind projects by 2020 is strongly affected
by the expiration of the Federal Production Tax Credit (PTC).
But this seems to ignore PTC's purpose of supporting the wind energy industry as it begins to expand, rather than subsidizing technology
indefinitely.
With the gradual withdrawal of PTC, combined with global technology cost reductions, wind energy will be able to stand on its own and compete with other technologies without subsidies or government support, which is already happening
globally.
”
The report also predicts that 5 GW of utility-scale solar PV will come online in 2019 and another 6 GW
in 2020.
In addition, by 2020, EIA expects to install another 9 GW of small-scale solar photovoltaic systems
.
Overall, renewables accounted for 17% of total electricity generation in 2018 and are expected to increase to 18% in 2019 and 20%
in 2020.
Hydropower accounts for 7% of total electricity generation and will remain at this level
in 2019-2020.
The EIA forecasts that U.
S.
coal production will decline 3 percent in 2019 to 729 million short tons (MMst) and then another 7 percent in 2020, following "the relatively weak competitiveness of coal compared to natural gas in the power sector, as well as the assumption
of declining demand for U.
S.
coal exports.
" Despite a 4% increase in total generation, coal consumption fell by 4% in 2018, while EIA expects coal consumption to decline by 8% in 2019 and another 7%
in 2020.
In addition, total utility-scale generation from natural gas plants is expected to increase from 35% in 2018 to 37% in 2020, while coal's forecast share will decline from 28% in 2018 to 24%
in 2020.
Nuclear power generation accounted for 19% in 2018 and will remain unchanged
through 2020.
According to the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration EIA's short-term energy outlook, SETO said that in 2019, U.
S.
wind power is expected to surpass hydropower for the first time and account for a larger proportion
of the domestic electricity mix.
Specifically, U.
S.
wind capacity is expected to increase from 96 GW at the end of 2018 to 107 GW by the end of 2019 and 114 GW by 2020, which means that 11 GW of new U.
S.
wind power will be added in 2019 and 7 GW
by 2020.
Notably, the Production Tax Credit (PTC) in the United States will have an impact
on the country's wind industry for years to come.
"The construction of new wind projects by 2020 is strongly affected
by the expiration of the Federal Production Tax Credit (PTC).
But this seems to ignore PTC's purpose of supporting the wind energy industry as it begins to expand, rather than subsidizing technology
indefinitely.
With the gradual withdrawal of PTC, combined with global technology cost reductions, wind energy will be able to stand on its own and compete with other technologies without subsidies or government support, which is already happening
globally.
”
The report also predicts that 5 GW of utility-scale solar PV will come online in 2019 and another 6 GW
in 2020.
In addition, by 2020, EIA expects to install another 9 GW of small-scale solar photovoltaic systems
.
Overall, renewables accounted for 17% of total electricity generation in 2018 and are expected to increase to 18% in 2019 and 20%
in 2020.
Hydropower accounts for 7% of total electricity generation and will remain at this level
in 2019-2020.
The EIA forecasts that U.
S.
coal production will decline 3 percent in 2019 to 729 million short tons (MMst) and then another 7 percent in 2020, following "the relatively weak competitiveness of coal compared to natural gas in the power sector, as well as the assumption
of declining demand for U.
S.
coal exports.
" Despite a 4% increase in total generation, coal consumption fell by 4% in 2018, while EIA expects coal consumption to decline by 8% in 2019 and another 7%
in 2020.
In addition, total utility-scale generation from natural gas plants is expected to increase from 35% in 2018 to 37% in 2020, while coal's forecast share will decline from 28% in 2018 to 24%
in 2020.
Nuclear power generation accounted for 19% in 2018 and will remain unchanged
through 2020.