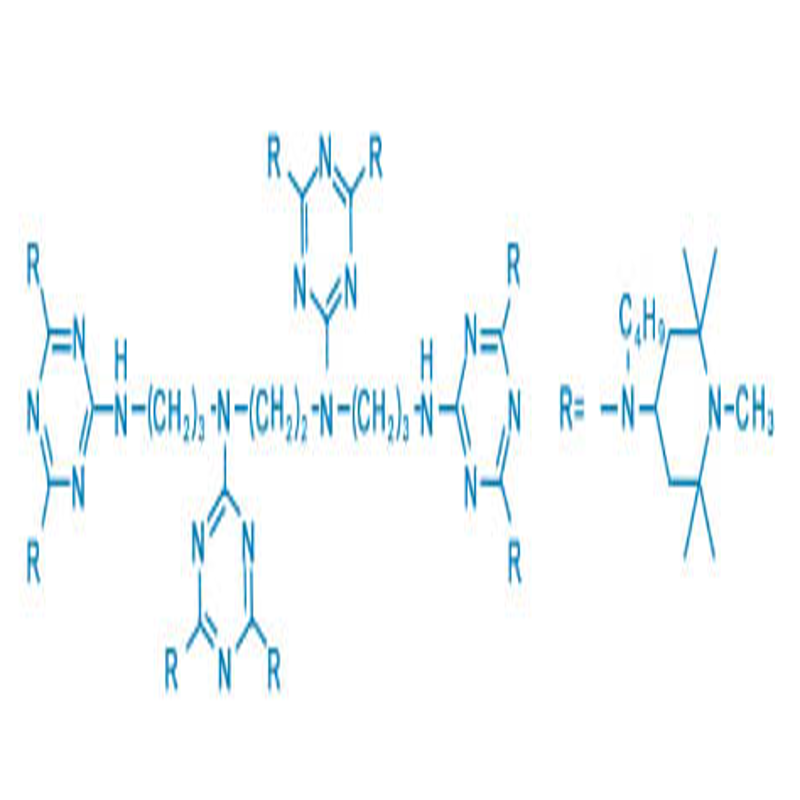
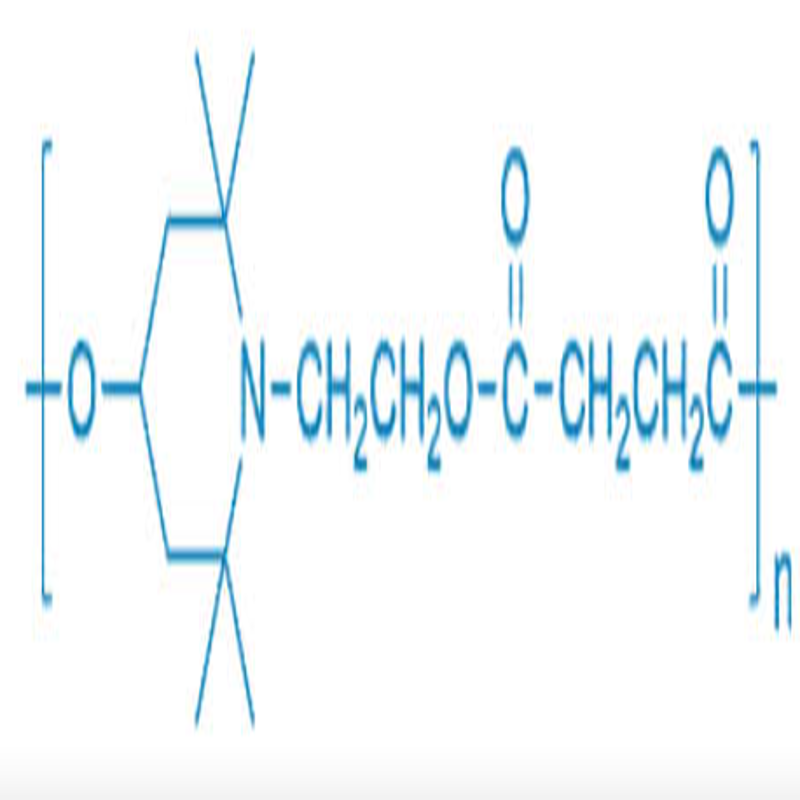
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Last year, U.
S.
fossil fuel consumption fell to its lowest level
since 1902.
In 2017, U.
S.
fossil fuel consumption fell to its lowest level since 1902
According to the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration (EIA), fossil fuel consumption fell
for the third consecutive year, driven by a slight decline in coal and natural gas consumption.
Coal consumption fell 2.
5 percent in 2017, nearly 40 percent
lower than it peaked in 2005.
Natural gas consumption fell by 1.
4% last year, but consumption has increased in 8 of the last 10 years, and gas consumption was twice
as high as coal last year.
Its growth was mainly due to the increased use of the electricity sector, with total natural gas consumption increasing by 24%
compared to 2005.
In 2017, the share of renewables, including hydropower, biomass, wind and solar, rose to 11.
3%, the highest level
since the late 1910s.
"The primary energy source in the United States has undergone many changes, from wood as a primary resource in the 18th and 19th centuries, to the use of coal and oil, to the rise of more modern nuclear power in the late 20th century and renewable energy
in the early 21st century," the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration states.
”
,
Last year, U.
S.
fossil fuel consumption fell to its lowest level
since 1902.
In 2017, U.
S.
fossil fuel consumption fell to its lowest level since 1902
S.
fossil fuel consumption fell to its lowest level since 1902
According to the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration (EIA), fossil fuel consumption fell
for the third consecutive year, driven by a slight decline in coal and natural gas consumption.
Coal consumption fell 2.
5 percent in 2017, nearly 40 percent
lower than it peaked in 2005.
Natural gas consumption fell by 1.
4% last year, but consumption has increased in 8 of the last 10 years, and gas consumption was twice
as high as coal last year.
Its growth was mainly due to the increased use of the electricity sector, with total natural gas consumption increasing by 24%
compared to 2005.
In 2017, the share of renewables, including hydropower, biomass, wind and solar, rose to 11.
3%, the highest level
since the late 1910s.
"The primary energy source in the United States has undergone many changes, from wood as a primary resource in the 18th and 19th centuries, to the use of coal and oil, to the rise of more modern nuclear power in the late 20th century and renewable energy
in the early 21st century," the U.
S.
Energy Information Administration states.
”
,