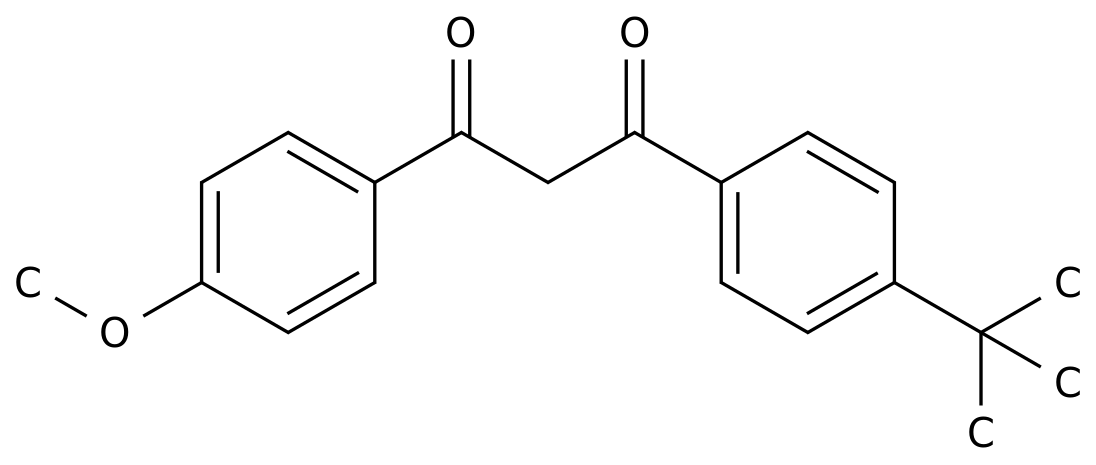
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), with private and state-owned Chinese companies actively taking advantage of the fast-growing renewable energy market, China has more than $12 billion in foreign wind investment activity in Europe and Australia, with most wind investment activity in Europe
.
IEEFA: China has invested more than $12 billion in wind power in Europe and Australia
"China is now an enabler of Europe's energy transition, and its international leadership in future low-emissions sectors is fully aligned
with efforts to increase China's global economic impact.
" IEEFA analyst Simon Nicholas said: "While the Belt and Road Initiative launched five years ago boosted China's outbound renewable energy investment, foreign renewable energy investment has now far exceeded the framework target
.
Nicholas said: "This is a superpower that is pushing its energy policy global
.
”
IEEFA's research brief says that China's foreign investment in renewable energy has increased as a result of the Belt and Road Initiative, but most of this investment is not in countries
bordering the Belt and Road.
The fact sheet builds on documents released in January and describes how China has become the world's leading renewable energy investor
.
Data shows that China's investment in new energy technology and resources was US$44 billion in 2017, up from US$32 billion
in 2016.
In 2017, the Chinese government began restructuring its power generation industry to reduce its reliance on coal and export renewable energy technologies, while continuing to promote its coal technologies
in developing foreign markets.
Between 2003 and 2017, China's overseas energy investment was dominated by hydropower and coal-fired power generation, and more recently wind and solar power stood out
due to technological advances, efficiency improvements and sharp cost declines.
However, while China's wind and solar investment in developed countries far exceeds that of BRI countries, coal-fired power generation activity remains high
in countries bordering the BRI and other developing countries, the fact sheet notes.
From 2003 to 2017, most of China's foreign power investment in Southeast Asia went to hydropower ($45 billion) and coal ($12 billion) projects, far more than China's wind investment
in the European Union ($6.
8 billion) and Australia ($50).
The briefing includes notes from Chinese companies, including China Nuclear Power Group, China Resources Power, China Shenhua Group, China Three Gorges, State Development and Investment Corporation, China Huadian Group and China Huaneng Group
.
,
According to the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), with private and state-owned Chinese companies actively taking advantage of the fast-growing renewable energy market, China has more than $12 billion in foreign wind investment activity in Europe and Australia, with most wind investment activity in Europe
.
IEEFA: China has invested more than $12 billion in wind power in Europe and Australia
IEEFA: China has invested more than $12 billion in wind power in Europe and Australia"China is now an enabler of Europe's energy transition, and its international leadership in future low-emissions sectors is fully aligned
with efforts to increase China's global economic impact.
" IEEFA analyst Simon Nicholas said: "While the Belt and Road Initiative launched five years ago boosted China's outbound renewable energy investment, foreign renewable energy investment has now far exceeded the framework target
.
Nicholas said: "This is a superpower that is pushing its energy policy global
.
”
IEEFA's research brief says that China's foreign investment in renewable energy has increased as a result of the Belt and Road Initiative, but most of this investment is not in countries
bordering the Belt and Road.
The fact sheet builds on documents released in January and describes how China has become the world's leading renewable energy investor
.
Data shows that China's investment in new energy technology and resources was US$44 billion in 2017, up from US$32 billion
in 2016.
In 2017, the Chinese government began restructuring its power generation industry to reduce its reliance on coal and export renewable energy technologies, while continuing to promote its coal technologies
in developing foreign markets.
Between 2003 and 2017, China's overseas energy investment was dominated by hydropower and coal-fired power generation, and more recently wind and solar power stood out
due to technological advances, efficiency improvements and sharp cost declines.
However, while China's wind and solar investment in developed countries far exceeds that of BRI countries, coal-fired power generation activity remains high
in countries bordering the BRI and other developing countries, the fact sheet notes.
From 2003 to 2017, most of China's foreign power investment in Southeast Asia went to hydropower ($45 billion) and coal ($12 billion) projects, far more than China's wind investment
in the European Union ($6.
8 billion) and Australia ($50).
The briefing includes notes from Chinese companies, including China Nuclear Power Group, China Resources Power, China Shenhua Group, China Three Gorges, State Development and Investment Corporation, China Huadian Group and China Huaneng Group
.
,