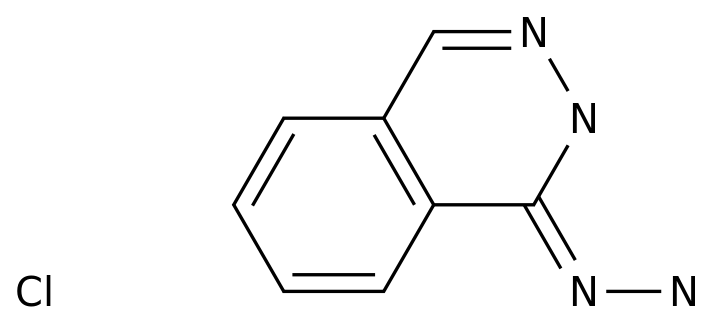
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Synthetic routes of Semiotiad are a set of chemical reactions used to produce this organic compound, which is commonly used as a building block in the chemical industry.
Semiotiad is a versatile compound that can be used in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other organic chemicals.
The synthetic routes for Semiotiad can vary depending on the starting materials and the desired product, but there are several common methods that are widely used in the industry.
One of the most common synthetic routes for Semiotiad involves the reaction of an aldehyde with a halogenated compound, such as chlorine or bromine.
This reaction is known as a halogenation reaction and typically involves the addition of the halogen molecule to the aldehyde molecule, resulting in the formation of a new compound.
The exact reaction conditions and reagents can vary depending on the specific starting materials and product, but the general process involves the addition of the halogen molecule to the aldehyde molecule, followed by subsequent chemical reactions to complete the synthesis of Semiotiad.
Another synthetic route for Semiotiad involves the reaction of an aldehyde with a nitrating agent, such as nitric acid.
This reaction is known as a nitration reaction and involves the addition of nitrate groups to the aldehyde molecule.
The exact reaction conditions and reagents can vary depending on the specific starting materials and product, but the general process involves the addition of nitric acid to the aldehyde molecule, followed by subsequent chemical reactions to complete the synthesis of Semiotiad.
Yet another synthetic route for Semiotiad involves the reaction of an aldehyde with a Grignard reagent.
A Grignard reagent is a type of organometallic compound that is commonly used in organic synthesis.
This reaction is known as a Grignard reaction and typically involves the formation of a new compound through the reaction of the aldehyde with the Grignard reagent.
The exact reaction conditions and reagents can vary depending on the specific starting materials and product, but the general process involves the addition of the Grignard reagent to the aldehyde molecule, followed by subsequent chemical reactions to complete the synthesis of Semiotiad.
Overall, there are several synthetic routes for Semiotiad, and the specific route used can vary depending on the starting materials and desired product.
However, these reactions all involve the addition of various groups to the aldehyde molecule, resulting in the formation of the final product.
Semiotiad is an important building block in the chemical industry, and its synthetic routes are widely used to produce a variety of chemicals and other organic compounds.