-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
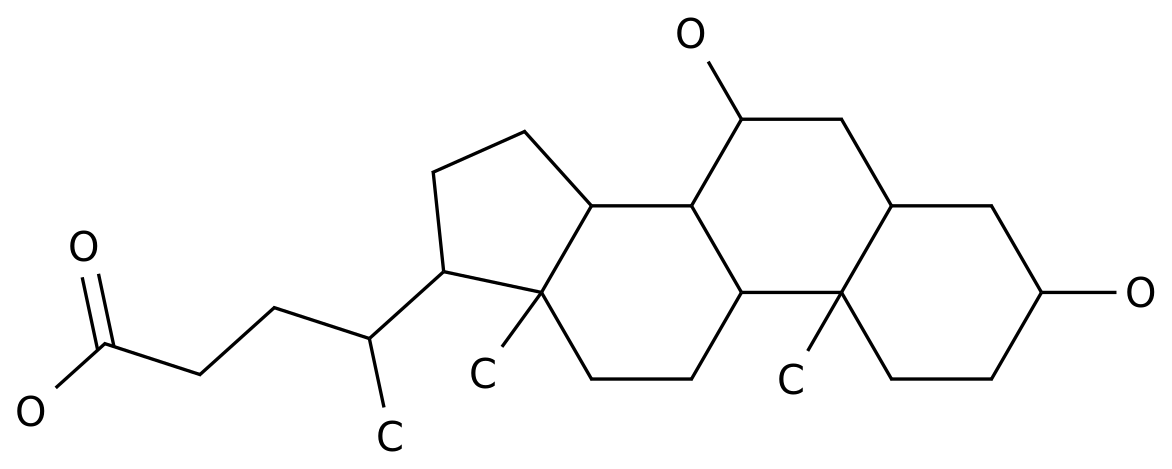
Diammonium glycyrrhizinate, also known as DG, is a natural compound that is extracted from the roots of the licorice plant.
It is widely used in the chemical industry as a intermediate for the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
There are several synthetic routes that are used to synthesize DG, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
One of the most common synthetic routes for DG is the "alkaline hydrolysis" method.
This method involves treating a mixture of glycyrrhizic acid and an amine, such as diammonium hydroxide, with lime and water.
The reaction results in the formation of DG, as well as a number of other compounds.
This method is relatively simple and inexpensive, but it requires a large amount of reagents and has a low yield of DG.
Another synthetic route for DG is the "nitrile oxide" method.
This method involves treating glycyrrhizic acid with nitrile oxide in the presence of a solvent such as ether or benzene.
The reaction results in the formation of DG, as well as a number of other compounds.
This method is more efficient and has a higher yield of DG than the alkaline hydrolysis method, but it requires the use of expensive reagents and can be more difficult to perform.
A third synthetic route for DG is the "esterification" method.
This method involves treating glycyrrhizic acid with an alcohol, such as ethanol or methanol, in the presence of a catalyst such as sodium hydroxide.
The reaction results in the formation of DG, as well as a number of other compounds.
This method is relatively simple and inexpensive, and can be performed at room temperature, but it has a low yield of DG.
Overall, the synthetic routes for DG vary in terms of their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of performance.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which method to use will depend on the specific needs of the chemical industry.
Regardless of the method used, DG is an important intermediate in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals and will continue to play a vital role in the chemical industry.