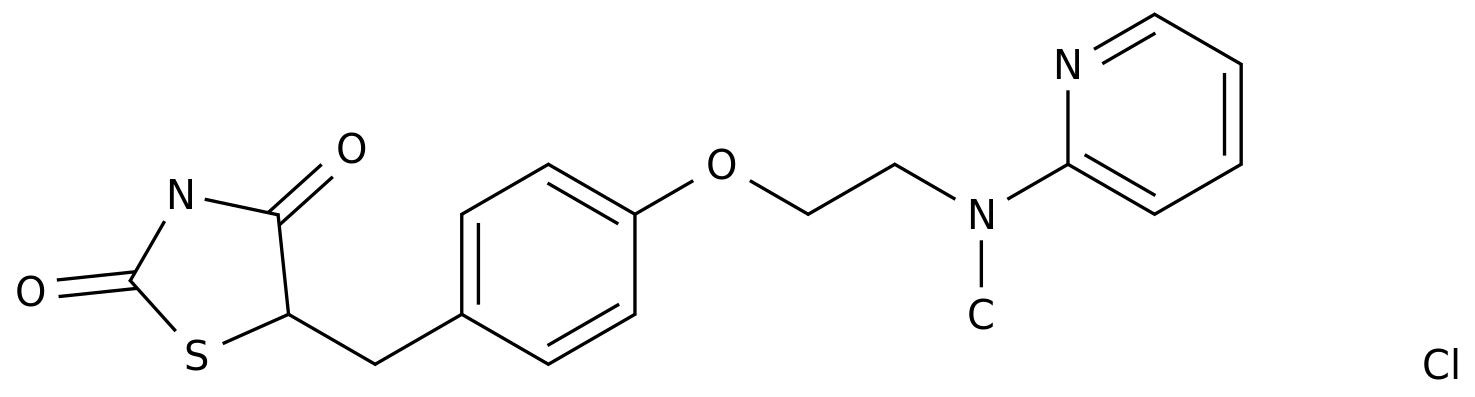
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
2-[4-[[[2-[3-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid is a synthetic compound that has gained significant attention in the chemical industry due to its unique properties and potential applications.
The compound is a derivative of 2-methylphenoxyacetic acid, which is a naturally occurring compound found in some plants.
The synthetic route to 2-[4-[[[2-[3-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid involves several steps, which can be divided into several categories based on the reaction conditions and the reagents used.
One of the most common methods for synthesizing 2-[4-[[[2-[3-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid involves a modified version of the Williamson ether synthesis.
In this method, 2-bromomethylphenol is treated with sodium hydroxide to generate the corresponding sodium salt, which is then treated with 2-[3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolic acid to form a Grignard reagent.
The Grignard reagent is then treated with 2-methyl-2-phenoxyacetic acid to form the final product.
Another common synthetic route involves the use of a modified version of the classical Fuchs synthesis.
In this method, 2-[3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolic acid is treated with sodium hydroxide to generate the corresponding sodium salt, which is then treated with 2-bromomethylphenol in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst.
The reaction is then complete by treating the resulting product with water to form the final product.
A third synthetic route involves the use of a modified version of the Mitsunobu reaction.
In this method, 2-[3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolic acid is treated with triphenylphosphine and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate in the presence of a base, such as triethylamine, to generate the corresponding azide.
The azide is then treated with 2-bromomethylphenol in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as aluminum chloride, to form the final product.
Overall, the synthesis of 2-[4-[[[2-[3-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-5-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid requires the use of several specialized reagents and conditions, and can be challenging to perform.
However, the compound has several unique properties that make it an attractive target for use in various industrial applications.