-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
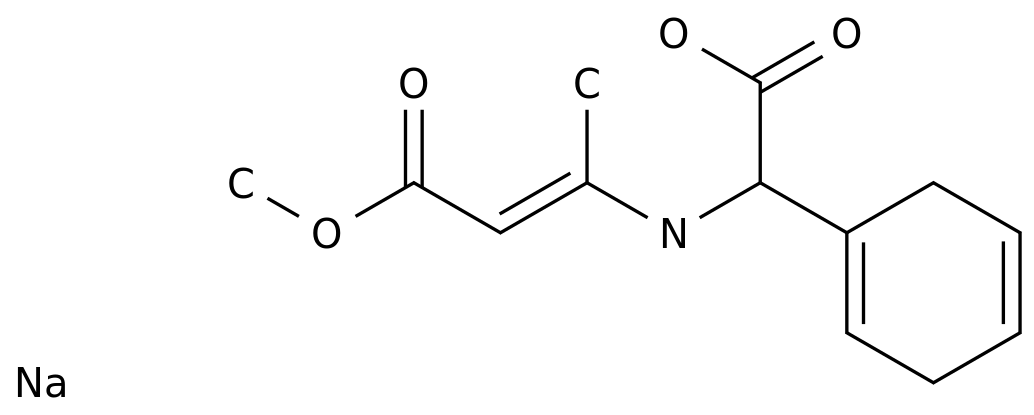
L-Aspartic acid, calcium salt (2:1) is a widely used intermediate chemical in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food additives.
The production process of L-Aspartic acid, calcium salt (2:1) involves several steps, including the synthesis of L-aspartic acid and its conversion into the calcium salt.
Step 1: Synthesis of L-Aspartic Acid
The synthesis of L-aspartic acid involves the use of two different methods, which are the chemical synthesis method and the biological synthesis method.
The chemical synthesis method involves the reaction of oxalic acid and ammonia, while the biological synthesis method involves the fermentation of a variety of carbon sources, such as corn starch or sugar cane.
Step 2: Purification of L-Aspartic Acid
After the synthesis of L-aspartic acid, it is necessary to purify the compound to remove any impurities that may have been introduced during the synthesis process.
This step is important to ensure the quality and purity of the final product.
There are several methods for purifying L-aspartic acid, including crystallization, filtration, and chromatography.
Step 3: Conversion of L-Aspartic Acid into Calcium Salt (2:1)
The conversion of L-aspartic acid into the calcium salt (2:1) involves the reaction of L-aspartic acid with calcium hydroxide.
The reaction takes place in a reaction vessel, and the reaction is exothermic, requiring careful temperature control to avoid excessive heat generation.
The reaction is typically carried out at a temperature of 80-120°C, and the reaction mixture is stirred continuously to ensure uniform mixing.
Step 4: Recrystallization
After the conversion of L-aspartic acid into the calcium salt (2:1), the product is typically purified by recrystallization.
This involves dissolving the calcium salt in a suitable solvent, such as water or ethanol, and allowing the solvent to evaporate slowly, resulting in the formation of crystals.
The crystals are then collected and dried, leaving behind a pure sample of the calcium salt (2:1).
Step 5: Characterization of the Product
The final step in the production process of L-Aspartic acid, calcium salt (2:1) is the characterization of the product.
This involves various tests, such as spectral analysis, elemental analysis, and chromatography, to determine the chemical properties and purity of the product.
This information is used to ensure the quality of the final product and to troubleshoot any problems that may arise during the production process.
In conclusion, the production process of L-Aspartic acid, calcium salt (2:1) involves several steps, including the synthesis of L-aspartic acid, its purification, conversion into the calcium salt, and recrystallization.
The final step is the characterization of the product, which is used to ensure its quality and purity.
The production of L-Aspartic acid, calcium salt (2:1) is a complex process that requires careful control and monitoring to ensure the quality of the final product.