-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
The production of copolymers is essential in the chemical industry as they are widely used in various applications.
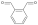
One such copolymer is dimethyl isophthalate-dimethyl terephthalate-ethylene glycol, which is commonly referred to as a polyester copolymer.
This copolymer is produced through a reaction between dimethyl isophthalate, dimethyl terephthalate, and ethylene glycol.
Dimethyl isophthalate and dimethyl terephthalate are both aromatic diacids, which are organic compounds that contain a benzene ring and two carboxyl groups.
These compounds are commonly used in the production of polyester fibers, films, and bottles.
Ethylene glycol, on the other hand, is an organic solvent that is used as a reactant in the production of polyester copolymers.
To produce the copolymer, the diacids and glycol are reacted in the presence of a catalyst, such as a metal alkoxide or a tin catalyst.
The reaction between the reactants results in the formation of the copolymer, which can then be purified and processed into the desired form.
The production of copolymers, such as dimethyl isophthalate-dimethyl terephthalate-ethylene glycol, is an efficient and cost-effective way of producing polyester materials.
Compared to traditional methods of producing polyester, such as the phthalic anhydride process, the copolymer method has several advantages.
One of the main advantages of the copolymer method is that it produces a more consistent and uniform material.
This is because the reaction between the reactants is more controlled, which results in fewer impurities and a higher quality product.
Furthermore, the copolymer method allows for the production of a wider range of polyester copolymers, which can be tailored to specific applications.
Another advantage of the copolymer method is that it is more environmentally friendly than traditional methods of producing polyester.
This is because the copolymer method produces less waste and emissions, and the copolymer can be recycled and reused.
Additionally, the use of ethylene glycol as a reactant in the production of the copolymer reduces the dependence on petroleum-based feedstocks, which is beneficial for both the environment and the economy.
In addition to their production advantages, polyester copolymers, such as dimethyl isophthalate-dimethyl terephthalate-ethylene glycol, are also widely used in various applications.
For example, they are commonly used in the production of polyester fibers, which are used in clothing and other textiles.
They are also used in the production of polyester films, which are used in packaging and other applications.
In the production of fibers, the copolymer is spun into fibers using a process such as melt spinning or solution spinning.
The fibers are then processed into yarns and woven or knitted into fabrics.
The properties of the copolymer, such as its melting point and thermal stability, can be tailored to specific applications, such as high-temperature use.
In the production of films, the copolymer is dissolved in a solvent, such as ethylene glycol, and then cast or extruded into the desired form.
The properties of the film, such as its thickness and clarity, can also be tailored to specific applications.
For example, the film can be used as a barrier layer in packaging to protect food from moisture and oxygen.
In conclusion, the production of dimethyl isophthalate-dimethyl terephthalate-ethylene glycol copolymer, also known as a polyester copolymer, is