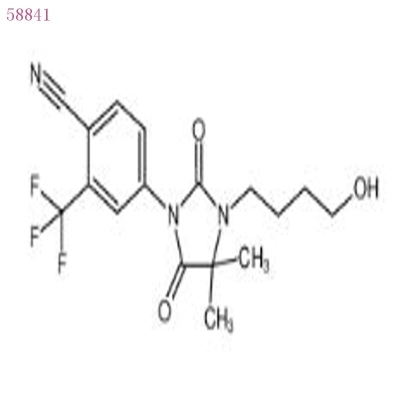
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Recently, the Agricultural Microbiology Team of the Institute of Vegetables of Hunan Academy of Agricultural Sciences published an article entitled "Insights into Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) Effects on Soil Nutrients and Pathogens from Pepper Mo" in the internationally renowned academic journal Microbiology Spectrum (IF=9.
0431) in the field of microbiology nocropping Soil under Anaerobic and Aerobic Conditions" research paper
.
This study reveals the regulatory mechanism
of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) to promote the activation of soil nutrients and inhibit soil-borne diseases in continuous cropping.
0431) in the field of microbiology nocropping Soil under Anaerobic and Aerobic Conditions" research paper
.
This study reveals the regulatory mechanism
of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) to promote the activation of soil nutrients and inhibit soil-borne diseases in continuous cropping.
PQQ is widely present in gram-negative bacteria, as a coenzyme substance involved in life metabolism processes, with water-soluble, thermal stability and antioxidant properties, widely used in
feed additives.
It is foreseeable that PQQ can affect soil micro-ecosystems as an exogenous soil additive, but the effects of PQQ on soil nutrient activation and soil pathogens in soils with continuous cropping disorders have not been reported
.
In view of the above background, the study used high-throughput sequencing technology, network analysis and structural equation model analysis to explore for the first time the effect of PQQ in soil nutrient activation and soil-borne pathogenic bacteria and related regulatory mechanisms
.
The results show that PQQ management measures reduce the abundance and variety of pathogenic microorganisms in continuous cropping soil by increasing soil pH and other ecological and environmental factors, balancing nitrogen, phosphorus and other nutrient factors in the soil, so as to reduce the occurrence
of soil-borne diseases.
At the same time, PQQ effectively activated soil nutrients by regulating the functional bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium, Sphingomonas, Gemmatimonas and Dyella in the enrichment of continuous crop soils, and improved the soil fertility
of continuous cropping.
This study provides a theoretical basis for the application of PQQ in the application of soil nutrient activation and soil-borne disease inhibition in continuous cropping in facilities, which is of great significance
for further promoting the research and development of efficient new agricultural microbial products.
feed additives.
It is foreseeable that PQQ can affect soil micro-ecosystems as an exogenous soil additive, but the effects of PQQ on soil nutrient activation and soil pathogens in soils with continuous cropping disorders have not been reported
.
In view of the above background, the study used high-throughput sequencing technology, network analysis and structural equation model analysis to explore for the first time the effect of PQQ in soil nutrient activation and soil-borne pathogenic bacteria and related regulatory mechanisms
.
The results show that PQQ management measures reduce the abundance and variety of pathogenic microorganisms in continuous cropping soil by increasing soil pH and other ecological and environmental factors, balancing nitrogen, phosphorus and other nutrient factors in the soil, so as to reduce the occurrence
of soil-borne diseases.
At the same time, PQQ effectively activated soil nutrients by regulating the functional bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium, Sphingomonas, Gemmatimonas and Dyella in the enrichment of continuous crop soils, and improved the soil fertility
of continuous cropping.
This study provides a theoretical basis for the application of PQQ in the application of soil nutrient activation and soil-borne disease inhibition in continuous cropping in facilities, which is of great significance
for further promoting the research and development of efficient new agricultural microbial products.
Dr.
Li Xin of the Institute of Vegetables is the first author, and Dr.
Tao Yu of the Institute of Vegetables and Dr.
Chen Jie of the Institute of Agriculture and Environmental Protection are the co-corresponding authors
.
The research was funded
by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, the Hunan Provincial High-tech Industry Science and Technology Innovation Leadership Program and the Changsha Science and Technology Bureau Project.
Li Xin of the Institute of Vegetables is the first author, and Dr.
Tao Yu of the Institute of Vegetables and Dr.
Chen Jie of the Institute of Agriculture and Environmental Protection are the co-corresponding authors
.
The research was funded
by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, the Hunan Provincial High-tech Industry Science and Technology Innovation Leadership Program and the Changsha Science and Technology Bureau Project.
Original link: https://pubmed.
ncbi.
nlm.
nih.
gov/35852313/
ncbi.
nlm.
nih.
gov/35852313/