-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
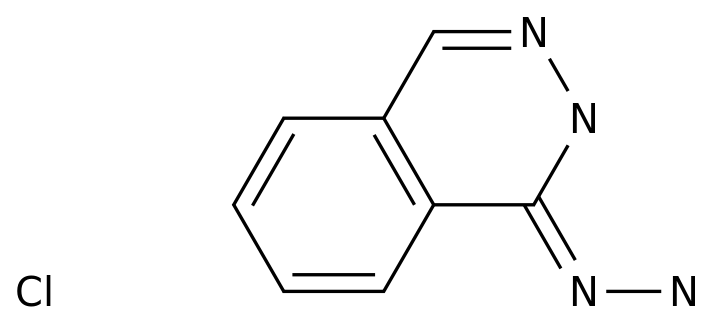
Synthetic routes of trimetazidine dihydrochloride are various methods used to synthesize the compound in the chemical industry.
Trimetazidine dihydrochloride is a pharmaceutical intermediate which is used in the production of some drugs.
It is a white or almost white, crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste.
It is soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.
The most common synthetic route for trimetazidine dihydrochloride is through the Williamson ether synthesis.
This reaction involves the reaction of a primary alcohol with a halogenated derivative of an alkane, such as chloroform.
The reaction results in the formation of an ether and a halide ion.
The halide ion is then displaced by an aqueous solution of a base, such as sodium hydroxide, resulting in the formation of the trimetazidine dihydrochloride.
Another common synthetic route for trimetazidine dihydrochloride is through the two-step synthesis.
This process involves the synthesis of an intermediate compound, known as 2-chloro-N-nitroso-N-methylbenzenamine, followed by its reaction with sodium hydroxide to form the trimetazidine dihydrochloride.
A more recent synthetic route for trimetazidine dihydrochloride is through the use of microwave-assisted synthesis.
This method involves the use of microwave radiation to accelerate the reaction sequence, resulting in a faster and more efficient synthesis of the compound.
This method has been shown to be more cost-effective, as it requires less time and fewer reagents compared to traditional synthesis methods.
In summary, there are several synthetic routes for trimetazidine dihydrochloride, including the Williamson ether synthesis, two-step synthesis, and microwave-assisted synthesis.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of synthetic route will depend on the specific needs of the chemical manufacturer.
Regardless of the synthetic route used, the result is a high-quality trimetazidine dihydrochloride that is used in the production of important pharmaceuticals.