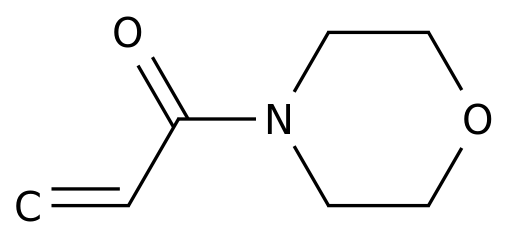
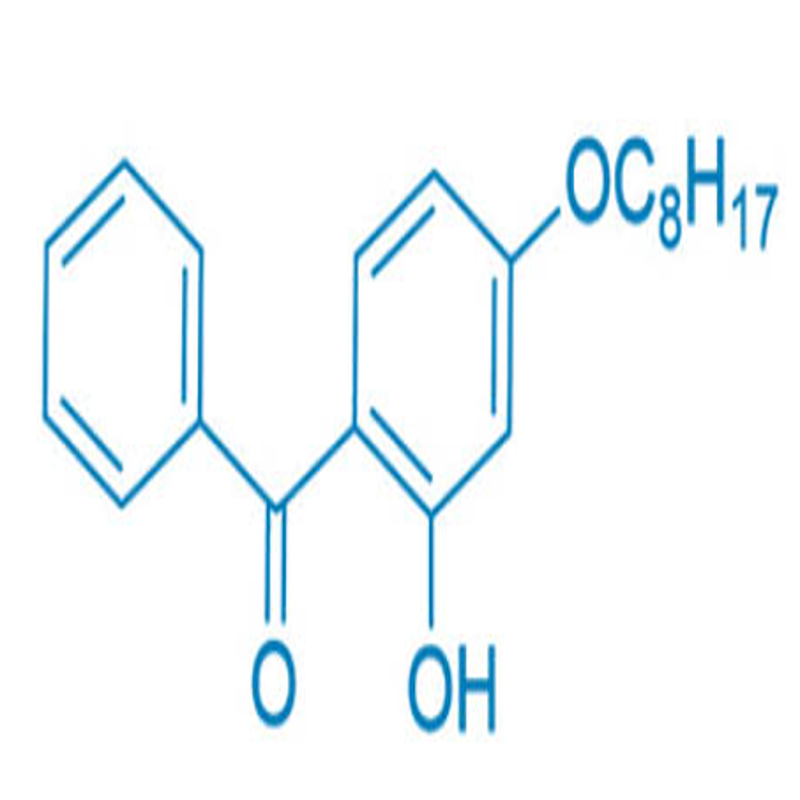
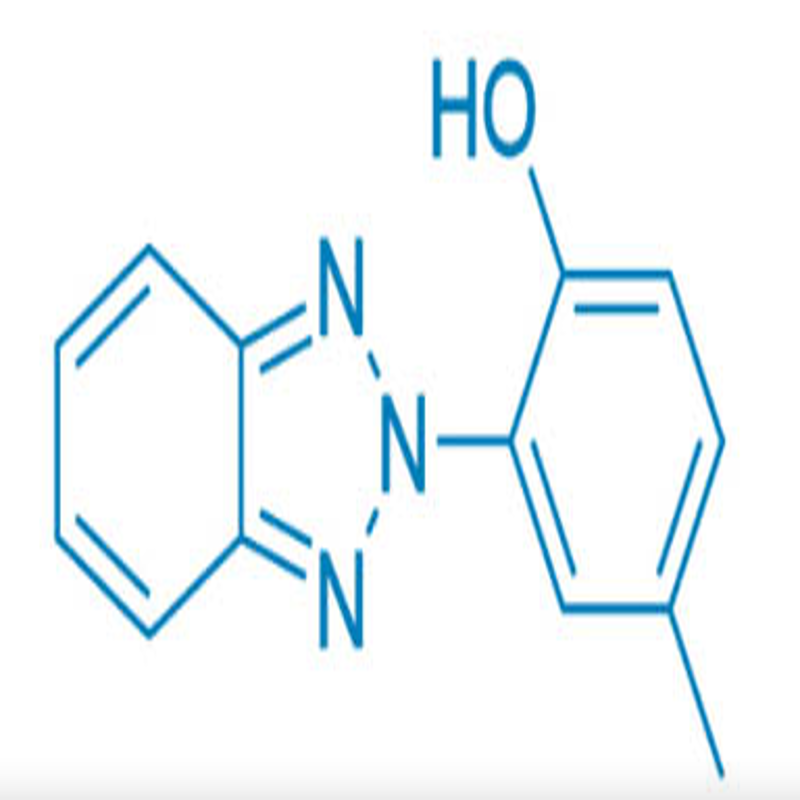
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Recently, the dollar has been soaring to record highs
against European and Asian currencies.
In this regard, ICIS experts pointed out that because major U.
S.
chemical companies not only make profits through exports, but also have a large number of production assets in Europe, Asia and other parts of the world, the strong performance of the US dollar will affect
the future earnings of US chemical companies.
A stronger dollar affects exports
ICIS said the dollar index has soared recently and is now up 22 percent
from a year ago.
In the Forex market, this is a huge move
.
Recently, the dollar hit a record high against the pound and a more than 20-year high
against the euro.
Major Asian currencies such as the yen and the won have also depreciated
sharply against the dollar.
The direct impact of the dollar's strength is multiple.
First, it makes U.
S.
exports more expensive and less competitive
in global markets.
Second, for performance in foreign markets, exchange rate losses converted into US dollars increased
.
Third, there is also the indirect effect that U.
S.
exports of manufactured goods, such as automobiles and their parts, machinery, electronic and computer products, medical equipment, aircraft and parts, are also uncompetitive
.
This means that production of these products in the United States will decline, and the demand for the chemicals and resins used will also decrease
.
Kevin Swift, senior economist at ICIS' global chemical business, said: "A stronger dollar makes U.
S.
-produced goods more expensive in foreign markets, so exports tend to decline
.
However, in the favor of U.
S.
chemical producers, oil and feedstocks are often priced
in dollars.
This drives up the cost
of raw materials for foreign producers.
U.
S.
manufacturing is also likely to feel more pressure in the domestic market due to cheaper
imports.
A stronger dollar will lower the price of foreign-produced goods shipped to the United States, so the volume of U.
S.
imports will tend to rise
.
”
Economies ranging from U.
S.
exports of chemicals and plastics to weak currencies in Europe and Asia are already challenging enough, and the impact
is exacerbated by a stronger dollar, ICIS said.
In 2021, U.
S.
chemical industry exports surged 22 percent to $153.
1 billion, according to the American Chemistry Council (ACC) mid-year outlook; Growth is expected to slow to 13% in 2022, with exports worth $173.
5 billion
.
Polyethylene (PE) is a major export of the United States, with major destinations being Asia, Europe and Latin America
.
The U.
S.
also imported $128.
3 billion in chemicals in 2021 and is expected to grow 20 percent to $153.
6 billion
in 2022, according to ACC.
Beautification enterprises frequently issue profit warnings
Major U.
S.
chemical companies with larger operations in Europe and Asia are or are about to experience more severe profit declines
due to currency issues that have slowed sales growth.
While not all companies specifically mention the exchange rate issue in their profit warnings, ICIS said it is undoubtedly a factor that will only exacerbate weakness
.
In its third-quarter earnings warning, Eastman Chemical singled out the strengthening of the U.
S.
dollar against multiple currencies, including the euro and yen, as one of
many factors that contributed to the company's lower-than-expected third-quarter earnings.
In 2021, about 26% of Eastman Chemical's sales revenue came from the EMEA market and 24% from the Asian market
.
Huntsman also lowered its third-quarter profit forecast due to high energy costs in Europe, lower-than-expected demand and slowing
economic growth in China.
According to 2021 sales revenue data, 27% of Huntsman's sales revenue comes from Europe and 30% from Asia
.
Chemours' earnings warning pointed to the continued deterioration of market demand for titanium dioxide, especially in Europe and Asia
.
In 2021, Chemours accounted for 22% of sales revenue in EMEA and 29%
in Asia.
Teno lowered its EBITDA forecast for the third quarter to $240 million ~$255 million from $275 million ~ $295 million in the previous period due to lower-than-expected volumes in Europe and Asia and higher
energy costs in Europe.
Based on sales in 2021, Teno accounted for 39% of total sales revenue in the EMEA market and 33%
in Asia.
Evante warned that third-quarter earnings would be lower than expected due to lower consumer confidence and demand in Europe, a weak economic recovery in Asia, weaker demand trends due to rising interest rates in the United States, and destocking
by global customers.
Evant highlighted headwinds in the foreign exchange market as the reason for the impact on
third-quarter profits.
About 25% of the company's sales revenue in 2021 came from Europe and 16% from Asia
.
Exchange rate effects are likely to continue
According to ICIS, the dollar is likely to continue to strengthen
as long as the Fed continues to raise interest rates in a more aggressive way than other national and regional central banks to curb inflation.
At present, the European Central Bank and the Bank of England have accelerated the pace of interest rate hikes, but the Bank of Japan has kept interest rates close to zero
.
The impact of the strength of the dollar exchange rate will continue
.
Paul Hodges, chairman of consultancy New Normal, highlighted a strong correlation
between real yields on European government bonds (adjusted for inflation) and the weakening of the euro against the dollar.
The low real yield of euro sovereign debt relative to US Treasuries has led to a sharp decline
in the euro.
This, in turn, has forced the ECB to follow the Fed's lead in raising interest rates in order to combat inflation
.
Major Latin American currencies, particularly the Brazilian real and the Mexican peso, have relatively strong exchange rates against the US dollar, so the regional foreign exchange adverse impact will be small
.
Since March 2021, Brazil's central bank has raised interest rates 12 times in a row and is considering ending the rate hike cycle
.
A sharp rise in the dollar's exchange rate could lead to further turmoil in financial markets, especially in emerging markets, where governments and businesses have taken on dollar-denominated debt that must be repaid
in dollars.
Mike Wilson, chief equity strategist at Morgan Stanley, noted on September 26 that the rising dollar is "creating an unsustainable situation for risky assets that have historically ended in financial or economic crises or both.
"
"For large amounts of dollar-denominated sovereign and corporate debt, especially in emerging markets, the cost of servicing these debts in local currency will rise
significantly," Swift said.
Many countries will have a harder time servicing these debts, and a strong dollar could trigger debt crises and geopolitical vulnerabilities
in many emerging countries.
”