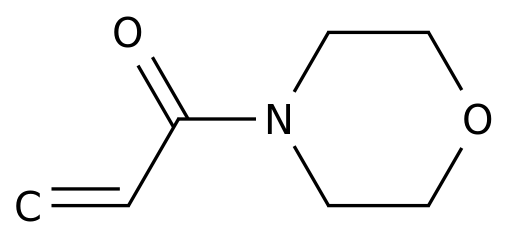
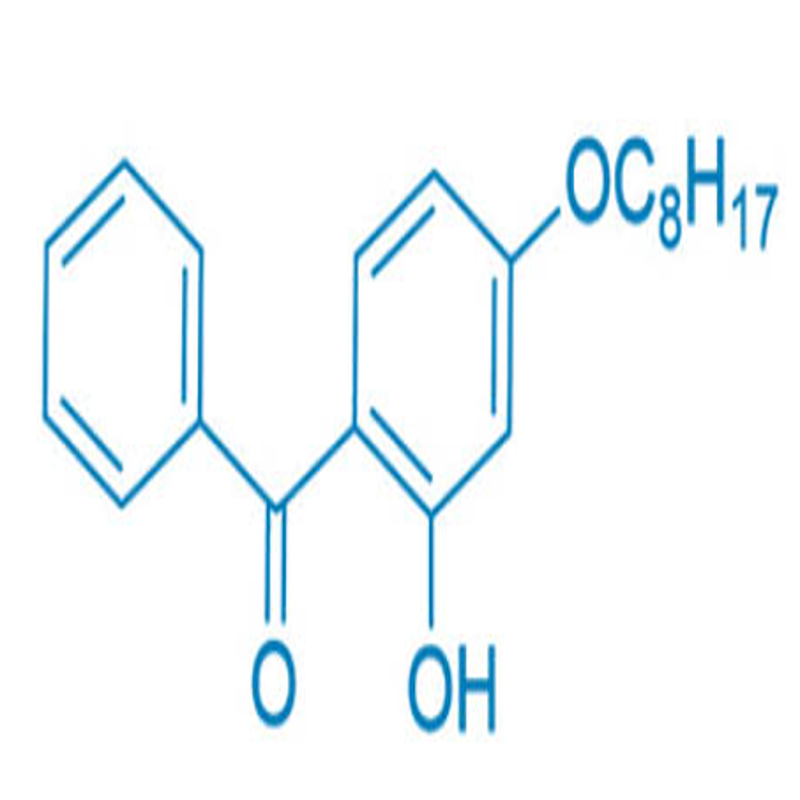
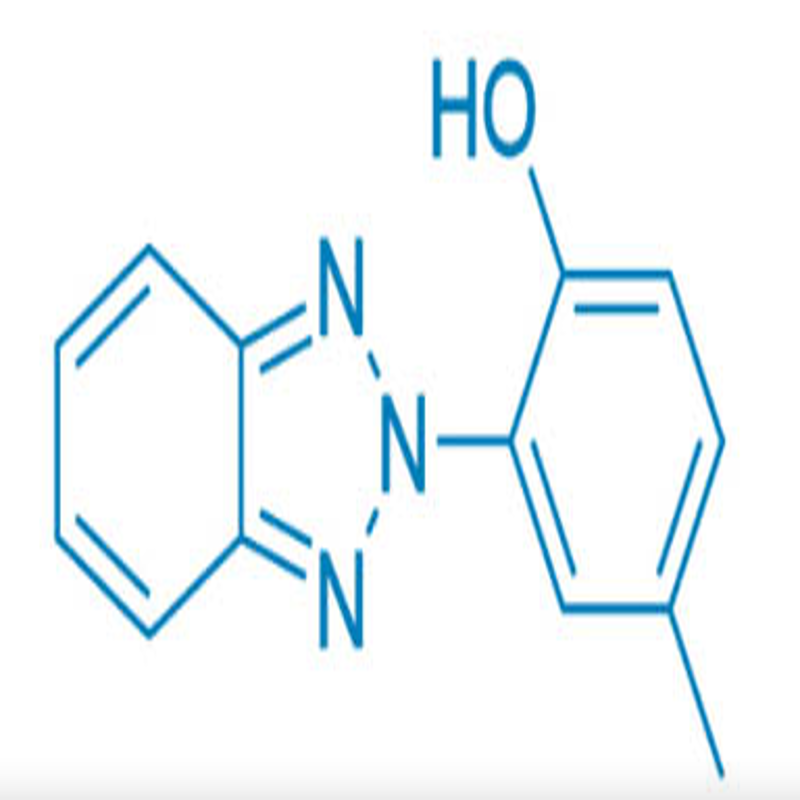
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
The Japanese government has established a new research entity
called the Lithium-ion Battery Technology and Evaluation Center Consortium (Libtec).
The Japanese government, in collaboration with major automakers such as Toyota, Honda, Panasonic and Yuasa, is tasked with advancing research into solid-state batteries that will cost less and have a wider range
of use than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
According to the Nikkei newspaper, the government will invest $14 million to be distributed to Libtec by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, whose members include Asahi Kasei and Toray Industries
.
The goal is to achieve solid-state batteries in the range of 550 kilometers by 2025 and 800 kilometers
by 2030.
In theory, solid-state batteries should be cheaper to manufacture and have a reduced
risk of fire compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
They may not need the complex temperature management or crash protection structures
that today's batteries have.
This could help make future lighter electric vehicles, which will translate into longer ranges
.
In 2013, Japanese battery manufacturers accounted for 70%
of the global market share.
Today, that percentage drops to 41 percent
.
China has grown from a market share of just 3% in 2013 to 26% market share today
.
Korean battery companies have also become a force
in the market during this time.
China is expected to add 80 million electric vehicles in the coming years, up from 650,000 in 2016
.
Germany's target for electric vehicles is 6 million, up from 70,000 in 2016
.
Japan hopes to see electric vehicles account for 30%
of sales by 2030.
Toyota is considered to be the current leader
in solid-state battery research in Japan.
The Libtec program hopes to leverage Toyota's expertise and combine it with new insights from other partners with a view to enabling Japan to regain its world leadership
in battery technology and manufacturing.
The Japanese government has established a new research entity
called the Lithium-ion Battery Technology and Evaluation Center Consortium (Libtec).
The Japanese government, in collaboration with major automakers such as Toyota, Honda, Panasonic and Yuasa, is tasked with advancing research into solid-state batteries that will cost less and have a wider range
of use than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
According to the Nikkei newspaper, the government will invest $14 million to be distributed to Libtec by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, whose members include Asahi Kasei and Toray Industries
.
The goal is to achieve solid-state batteries in the range of 550 kilometers by 2025 and 800 kilometers
by 2030.
In theory, solid-state batteries should be cheaper to manufacture and have a reduced
risk of fire compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
They may not need the complex temperature management or crash protection structures
that today's batteries have.
This could help make future lighter electric vehicles, which will translate into longer ranges
.
In 2013, Japanese battery manufacturers accounted for 70%
of the global market share.
Today, that percentage drops to 41 percent
.
China has grown from a market share of just 3% in 2013 to 26% market share today
.
Korean battery companies have also become a force
in the market during this time.
China is expected to add 80 million electric vehicles in the coming years, up from 650,000 in 2016
.
Germany's target for electric vehicles is 6 million, up from 70,000 in 2016
.
Japan hopes to see electric vehicles account for 30%
of sales by 2030.
Toyota is considered to be the current leader
in solid-state battery research in Japan.
The Libtec program hopes to leverage Toyota's expertise and combine it with new insights from other partners with a view to enabling Japan to regain its world leadership
in battery technology and manufacturing.