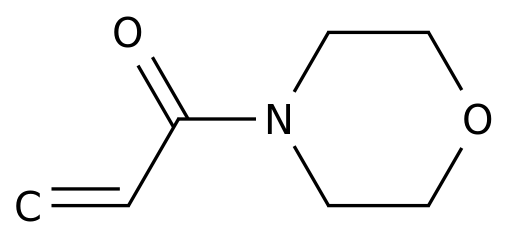
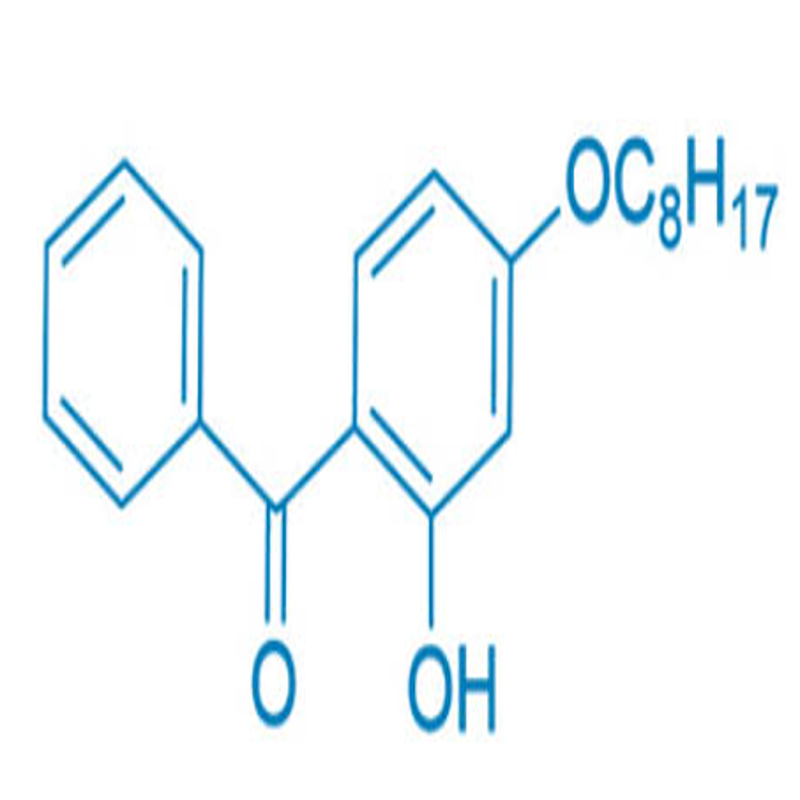
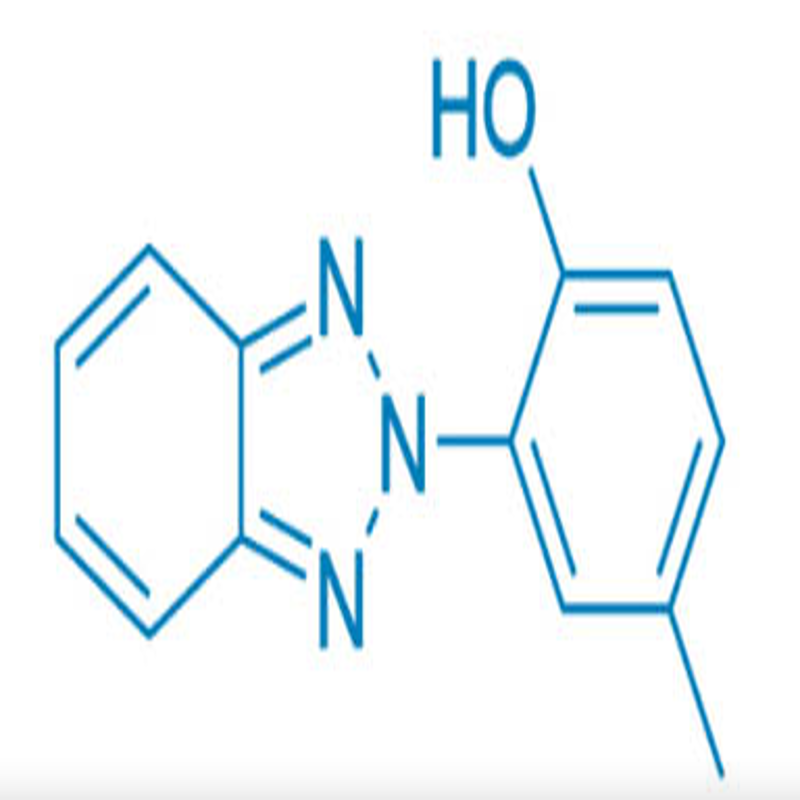
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems (MHPS) and Magnum Development announced a plan
to launch an Advanced Clean Energy Storage (ACES) program in Central Utah.
As the largest project of its kind in the world, ACES plans to develop 1,000 megawatts of 100% clean energy storage, thereby deploying technologies and strategies
essential for the decarbonized future of the Western U.
S.
grid.
According to researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, carbon emissions from the U.
S.
power sector have fallen 30 percent since 2005 as a combination of natural gas and renewables replaced retired coal-fired power plants
.
MHPS has played an important role in this transformation, becoming the global market share leader
for heavy-duty gas turbines last year.
As a next step in decarbonization, MHPS has developed gas turbine technology that enables blends of renewable hydrogen and natural gas to produce power
with lower carbon emissions.
The MHPS technology roadmap aims to use 100% renewable hydrogen as a fuel source, which will enable gas turbines to generate zero-carbon electricity
.
Magnum Development owns and controls the only known "Gulf Coast" style high-quality salt resource
in the western United States.
With five salt caverns already used for liquid fuel storage, Magnum is continuing to develop compressed air storage and renewable hydrogen storage options
.
Located near the Intermountain Power Project, the Magnum facility is ideally located for seamless integration with the power grid in the western United States using existing infrastructure
.
ACES plans to initially develop enough energy storage to fully meet the electricity needs of 150,000 homes for a year, and will deploy four types of clean energy storage
at the utility scale.
These energy storage technologies include renewable hydrogen, compressed air energy storage, large flow batteries, and solid oxide fuel cells
.
The ACES project will design, finance, build, own and operate a facility
located in Millard County, Utah.
In the coming weeks and months, other strategic and financial partners will be invited to participate
.
Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems (MHPS) and Magnum Development announced a plan
to launch an Advanced Clean Energy Storage (ACES) program in Central Utah.
As the largest project of its kind in the world, ACES plans to develop 1,000 megawatts of 100% clean energy storage, thereby deploying technologies and strategies
essential for the decarbonized future of the Western U.
S.
grid.
According to researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, carbon emissions from the U.
S.
power sector have fallen 30 percent since 2005 as a combination of natural gas and renewables replaced retired coal-fired power plants
.
MHPS has played an important role in this transformation, becoming the global market share leader
for heavy-duty gas turbines last year.
As a next step in decarbonization, MHPS has developed gas turbine technology that enables blends of renewable hydrogen and natural gas to produce power
with lower carbon emissions.
The MHPS technology roadmap aims to use 100% renewable hydrogen as a fuel source, which will enable gas turbines to generate zero-carbon electricity
.
Magnum Development owns and controls the only known "Gulf Coast" style high-quality salt resource
in the western United States.
With five salt caverns already used for liquid fuel storage, Magnum is continuing to develop compressed air storage and renewable hydrogen storage options
.
Located near the Intermountain Power Project, the Magnum facility is ideally located for seamless integration with the power grid in the western United States using existing infrastructure
.
ACES plans to initially develop enough energy storage to fully meet the electricity needs of 150,000 homes for a year, and will deploy four types of clean energy storage
at the utility scale.
These energy storage technologies include renewable hydrogen, compressed air energy storage, large flow batteries, and solid oxide fuel cells
.
The ACES project will design, finance, build, own and operate a facility
located in Millard County, Utah.
In the coming weeks and months, other strategic and financial partners will be invited to participate
.