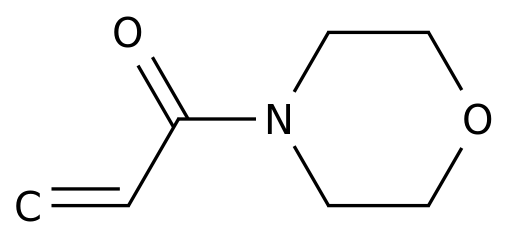
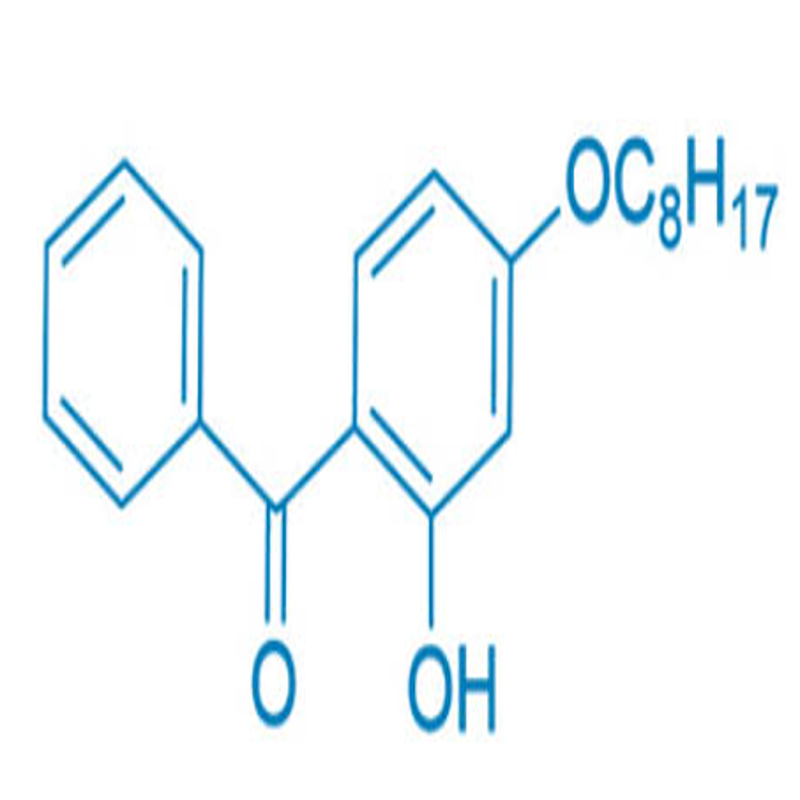
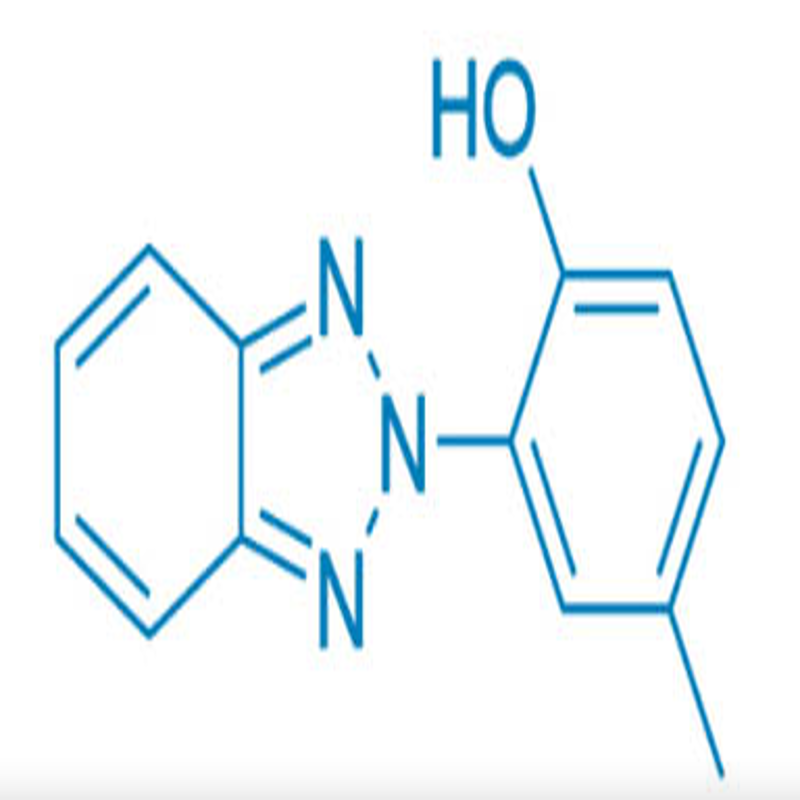
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
New figures released by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) show that last year's record for renewables was broken across the board, as renewables produced almost 37% of the UK's electricity
.
According to the data, renewable energy generation in the UK reached a record high of 36.
9% in 2019, of which wind power contributed 20%, which is also the highest proportion of wind power in history, including onshore wind power 9.
9% and offshore wind power 9.
9%.
In 2019, wind energy generated 32TWh
.
By the end of 2019, renewable energy generation capacity grew to 47.
4GW, up 6.
9%
from the same period last year.
Overall, low-carbon generation increased in 2019, ensuring a record 54.
2%
of renewables and nuclear energy combined.
Nuclear energy provides 17.
4 percent, natural gas 40.
9 percent and coal only 2.
1 percent
.
The growth of renewable energy has reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 3.
6% from 2018 and nearly 28%
since 2010.
Energy Minister Kwasi Kwarteng welcomed the news, especially during the uncertain times
caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK.
Kwasi Kwarteng said: "These new figures show that the UK has made extraordinary progress in tackling climate change, with emissions falling by 45%
since 1990.
With record-breaking levels of renewable energy generation on the grid, we can make the most of these efforts
in the coming months and years.
”
Overall, electricity production in the UK fell slightly compared to 2018, when 324TWh
was generated for the whole of 2019.
Energy efficiency measures contribute to this, but are also offset
by the transition to electric vehicles and electric heating.
Melanie Onn, deputy chief executive of RenewableUK, said the figures showed that the energy system was changing dramatically, with "low-cost renewables leading the way
.
" This trend will continue as we build a modern energy system, shifting away from fossil fuels to reach net zero emissions
as soon as possible.
In addition to wind energy, we will use innovative technologies such as renewable hydrogen and avionics, and expand battery storage
.
”
"Low-cost renewable energy is at the heart of the Government's energy strategy and our industry will grow rapidly
in the coming years as our domestic supply chain expands and we continue to capture multi-billion pound of export opportunities around the world.
"
Meanwhile, the National Grid survey found that throughout the 12 months of 2019, 48.
5% of the country's electricity came from zero-carbon sources, including wind farms, solar and nuclear, as well as energy
imported from the undersea interconnection.
Over the same period, 43% of the UK's electricity came from fossil fuels, mainly natural gas, with the remaining 8.
5% generated
by biomass.
New figures released by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) show that last year's record for renewables was broken across the board, as renewables produced almost 37% of the UK's electricity
.
According to the data, renewable energy generation in the UK reached a record high of 36.
9% in 2019, of which wind power contributed 20%, which is also the highest proportion of wind power in history, including onshore wind power 9.
9% and offshore wind power 9.
9%.
In 2019, wind energy generated 32TWh
.
By the end of 2019, renewable energy generation capacity grew to 47.
4GW, up 6.
9%
from the same period last year.
Overall, low-carbon generation increased in 2019, ensuring a record 54.
2%
of renewables and nuclear energy combined.
Nuclear energy provides 17.
4 percent, natural gas 40.
9 percent and coal only 2.
1 percent
.
The growth of renewable energy has reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 3.
6% from 2018 and nearly 28%
since 2010.
Energy Minister Kwasi Kwarteng welcomed the news, especially during the uncertain times
caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK.
Kwasi Kwarteng said: "These new figures show that the UK has made extraordinary progress in tackling climate change, with emissions falling by 45%
since 1990.
With record-breaking levels of renewable energy generation on the grid, we can make the most of these efforts
in the coming months and years.
”
Overall, electricity production in the UK fell slightly compared to 2018, when 324TWh
was generated for the whole of 2019.
Energy efficiency measures contribute to this, but are also offset
by the transition to electric vehicles and electric heating.
Melanie Onn, deputy chief executive of RenewableUK, said the figures showed that the energy system was changing dramatically, with "low-cost renewables leading the way
.
" This trend will continue as we build a modern energy system, shifting away from fossil fuels to reach net zero emissions
as soon as possible.
In addition to wind energy, we will use innovative technologies such as renewable hydrogen and avionics, and expand battery storage
.
”
"Low-cost renewable energy is at the heart of the Government's energy strategy and our industry will grow rapidly
in the coming years as our domestic supply chain expands and we continue to capture multi-billion pound of export opportunities around the world.
"
Meanwhile, the National Grid survey found that throughout the 12 months of 2019, 48.
5% of the country's electricity came from zero-carbon sources, including wind farms, solar and nuclear, as well as energy
imported from the undersea interconnection.
Over the same period, 43% of the UK's electricity came from fossil fuels, mainly natural gas, with the remaining 8.
5% generated
by biomass.