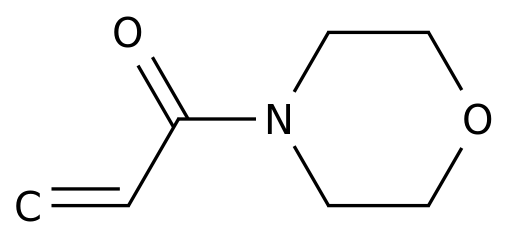
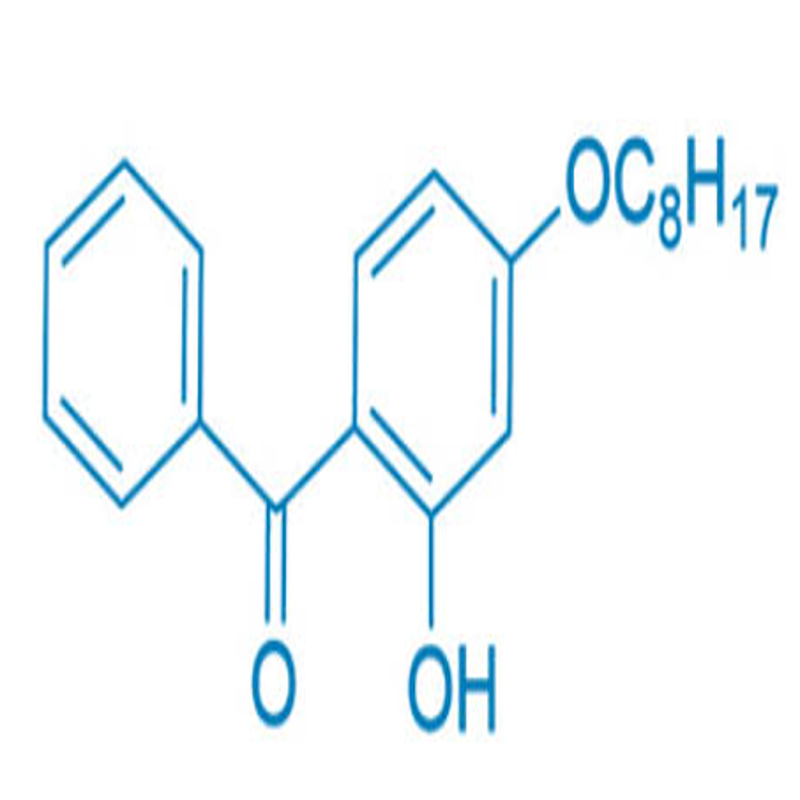
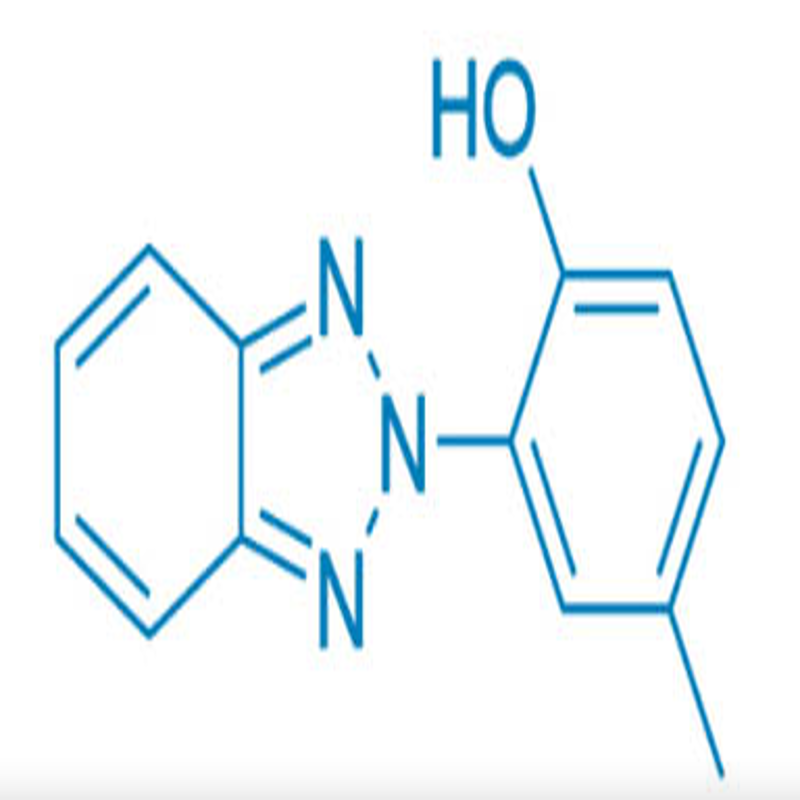
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to the latest data released by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, global investment in new renewable energy capacity reached $2.
6 trillion between 2010 and 2019, of which more solar power capacity will be installed than any other power generation technology
.
According to the 2019 Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment report, released ahead of the UN Global Climate Action Summit, the investment increased renewable energy capacity (excluding large hydropower) capacity to 1,650 GW (by the end of this year)
from 414 GW at the end of 2009.
Over the past decade, solar power has accounted for half of the investment, totaling $1.
3 trillion
.
The installed solar capacity will increase from 25 GW in 2010 to 663 GW (by the end of this year), enough to meet the annual electricity needs
of nearly 100 million households in the United States.
In 2018, the proportion of renewable energy in the global electricity mix reached 12.
9%, a significant increase
from 11.
6% in the previous year.
At the same time, this also reduces CO2 emissions
by 2 billion tons.
In 2018, total emissions from the power sector were 13.
7 billion tons
.
Including all major power generation technologies (fossil and zero-carbon), a ten-year net installed capacity of 2,366 GW will be installed, with solar accounting for the largest single share (663 GW) and coal taking second place (529 GW), followed by wind (487 GW) and natural gas (438 GW).
The cost competitiveness of renewable energy has also risen
sharply over the decade.
Since 2009, the average cost of electricity for solar PV (a measure that enables a continuous comparison of different power generation methods) has fallen by 81%, and onshore wind by 46%.
UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen said, "Investing in renewable energy is investing in a sustainable and profitable future
.
But we cannot be complacent
.
During this period, emissions from the global power sector increased by about 10%.
It is clear that if we are to meet international climate and development goals, we need to rapidly accelerate the global shift to renewable energy
.
”
Global investment in renewable energy reached $272.
9 billion in 2018.
While this was down 12 percent from the previous year, 2018 was the ninth consecutive year that capacity investment exceeded $200 billion and the fifth consecutive year that exceeded $250 billion
.
That's also three times
the total global investment in coal and gas-fired power capacity.
Despite the continued decline in the cost of capital for solar and wind projects, and policy changes affecting investment in China in the second half of the year, 2018 was still a strong year: a record 167 GW of new renewable energy capacity was completed, up from 160 GW
in 2017.
In terms of countries and regions, China is still in the lead
.
China has been the largest investor in renewable energy capacity over the past decade, committing $758 billion between 2010 and the first half of 2019, with the United States in second place at $356 billion and Japan third at $202 billion
.
Over the same period, European investment in renewable energy reached US$698 billion, with Germany contributing the most with US$179 billion and the UK US$122 billion
.
While China remained the largest single investor in 2018, global renewable energy investment is expanding, with 29 countries and territories each investing more than $1 billion, compared to 25 in 2017
.
According to the latest data released by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, global investment in new renewable energy capacity reached $2.
6 trillion between 2010 and 2019, of which more solar power capacity will be installed than any other power generation technology
.
According to the 2019 Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment report, released ahead of the UN Global Climate Action Summit, the investment increased renewable energy capacity (excluding large hydropower) capacity to 1,650 GW (by the end of this year)
from 414 GW at the end of 2009.
Over the past decade, solar power has accounted for half of the investment, totaling $1.
3 trillion
.
The installed solar capacity will increase from 25 GW in 2010 to 663 GW (by the end of this year), enough to meet the annual electricity needs
of nearly 100 million households in the United States.
In 2018, the proportion of renewable energy in the global electricity mix reached 12.
9%, a significant increase
from 11.
6% in the previous year.
At the same time, this also reduces CO2 emissions
by 2 billion tons.
In 2018, total emissions from the power sector were 13.
7 billion tons
.
Including all major power generation technologies (fossil and zero-carbon), a ten-year net installed capacity of 2,366 GW will be installed, with solar accounting for the largest single share (663 GW) and coal taking second place (529 GW), followed by wind (487 GW) and natural gas (438 GW).
The cost competitiveness of renewable energy has also risen
sharply over the decade.
Since 2009, the average cost of electricity for solar PV (a measure that enables a continuous comparison of different power generation methods) has fallen by 81%, and onshore wind by 46%.
UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen said, "Investing in renewable energy is investing in a sustainable and profitable future
.
But we cannot be complacent
.
During this period, emissions from the global power sector increased by about 10%.
It is clear that if we are to meet international climate and development goals, we need to rapidly accelerate the global shift to renewable energy
.
”
Global investment in renewable energy reached $272.
9 billion in 2018.
While this was down 12 percent from the previous year, 2018 was the ninth consecutive year that capacity investment exceeded $200 billion and the fifth consecutive year that exceeded $250 billion
.
That's also three times
the total global investment in coal and gas-fired power capacity.
Despite the continued decline in the cost of capital for solar and wind projects, and policy changes affecting investment in China in the second half of the year, 2018 was still a strong year: a record 167 GW of new renewable energy capacity was completed, up from 160 GW
in 2017.
In terms of countries and regions, China is still in the lead
.
China has been the largest investor in renewable energy capacity over the past decade, committing $758 billion between 2010 and the first half of 2019, with the United States in second place at $356 billion and Japan third at $202 billion
.
Over the same period, European investment in renewable energy reached US$698 billion, with Germany contributing the most with US$179 billion and the UK US$122 billion
.
While China remained the largest single investor in 2018, global renewable energy investment is expanding, with 29 countries and territories each investing more than $1 billion, compared to 25 in 2017
.