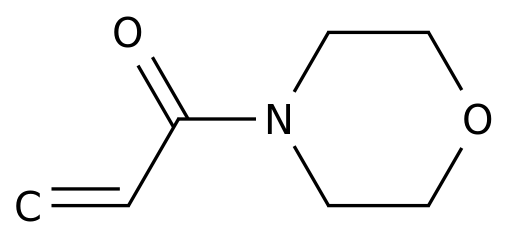
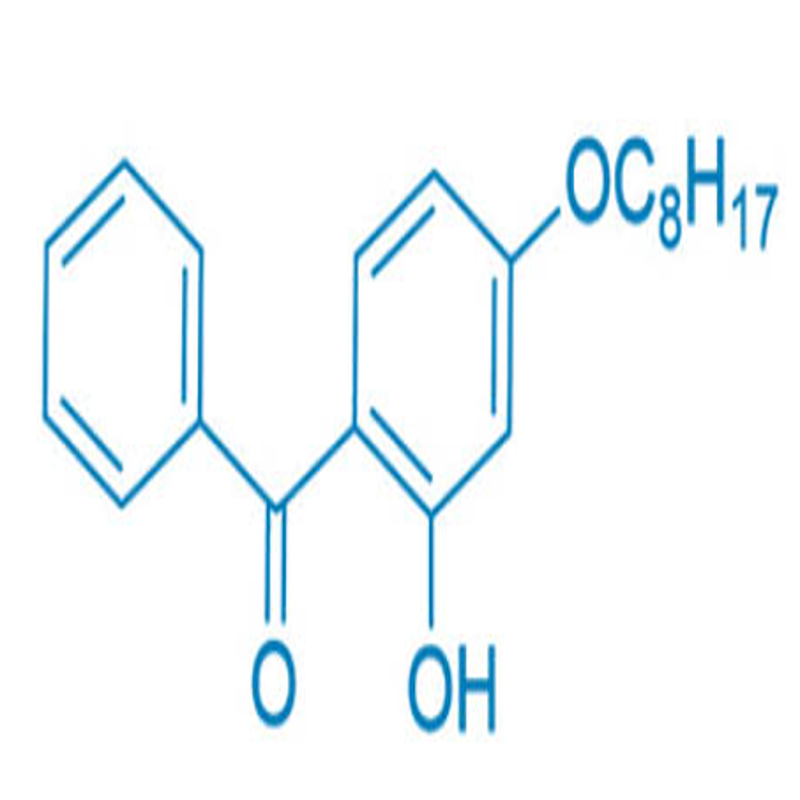
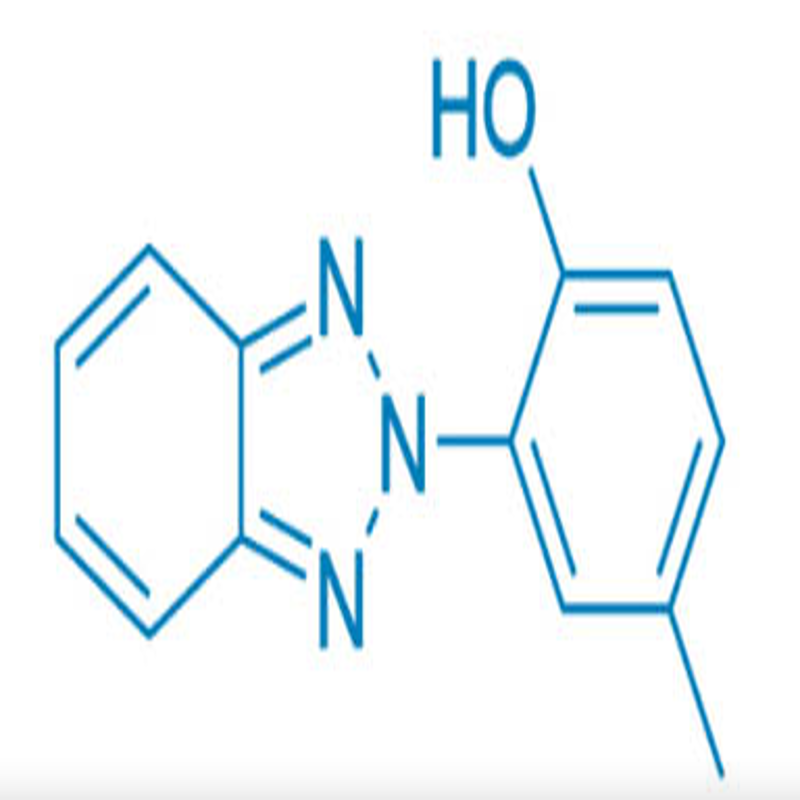
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to the Economic Times, India will produce 75% of its electricity
from renewable sources.
Of this, 34% comes from solar energy and 32% from wind energy
.
BNEF's Bloomberg New Energy Outlook 2018 report says wind and solar will soar to nearly 50% of the world's electricity generation by 2050 due to dramatically falling costs, as well as the emergence of cheaper batteries capable of generating electricity storage and offloading to meet demand and supply
.
The head of BNEF India Research said: "We expect cheap renewable energy and batteries to reshape the entire power system
.
In the future we see growth in new generation assets, significant reductions in the cost of wind energy, and renewables will provide 62% of electricity in China and 75% in India by 2050
.
The Asia-Pacific region invests almost as much in power plants, with the rest of the world reaching 49% with China, with India accounting for 29%
of total regional investment.
”
He further added that the arrival of cheap battery storage means that it is increasingly possible to provide electricity through wind and solar power, so these technologies can help meet demand
even when the wind does not blow the sun.
"The result will be that renewables increasingly occupy existing coal, gas and nuclear markets
," he stressed.
”
The report predicts that $11.
5 trillion will be invested globally on new generation capacity between 2018 and 2050, of which $8.
4 trillion will be spent on wind and solar and $1.
5 trillion on other zero-carbon technologies such as hydropower and nuclear power
.
This investment will increase global solar photovoltaic capacity by 17 times and wind power capacity by 6 times
.
It is expected that by 2050, the levelized cost of electricity for new PV plants will further fall by 71%, while the cost of onshore wind power will further fall by 58%.
Between 2009 and 2018, the cost of electricity reduction for these two technologies was 77% and 41%,
respectively.
:/, please indicate the source for reprinting)
According to the Economic Times, India will produce 75% of its electricity
from renewable sources.
Of this, 34% comes from solar energy and 32% from wind energy
.
BNEF's Bloomberg New Energy Outlook 2018 report says wind and solar will soar to nearly 50% of the world's electricity generation by 2050 due to dramatically falling costs, as well as the emergence of cheaper batteries capable of generating electricity storage and offloading to meet demand and supply
.
The head of BNEF India Research said: "We expect cheap renewable energy and batteries to reshape the entire power system
.
In the future we see growth in new generation assets, significant reductions in the cost of wind energy, and renewables will provide 62% of electricity in China and 75% in India by 2050
.
The Asia-Pacific region invests almost as much in power plants, with the rest of the world reaching 49% with China, with India accounting for 29%
of total regional investment.
”
He further added that the arrival of cheap battery storage means that it is increasingly possible to provide electricity through wind and solar power, so these technologies can help meet demand
even when the wind does not blow the sun.
"The result will be that renewables increasingly occupy existing coal, gas and nuclear markets
," he stressed.
”
The report predicts that $11.
5 trillion will be invested globally on new generation capacity between 2018 and 2050, of which $8.
4 trillion will be spent on wind and solar and $1.
5 trillion on other zero-carbon technologies such as hydropower and nuclear power
.
This investment will increase global solar photovoltaic capacity by 17 times and wind power capacity by 6 times
.
It is expected that by 2050, the levelized cost of electricity for new PV plants will further fall by 71%, while the cost of onshore wind power will further fall by 58%.
Between 2009 and 2018, the cost of electricity reduction for these two technologies was 77% and 41%,
respectively.
:/, please indicate the source for reprinting)
/