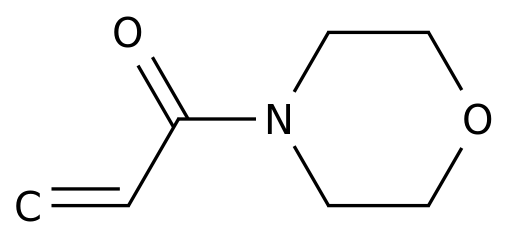
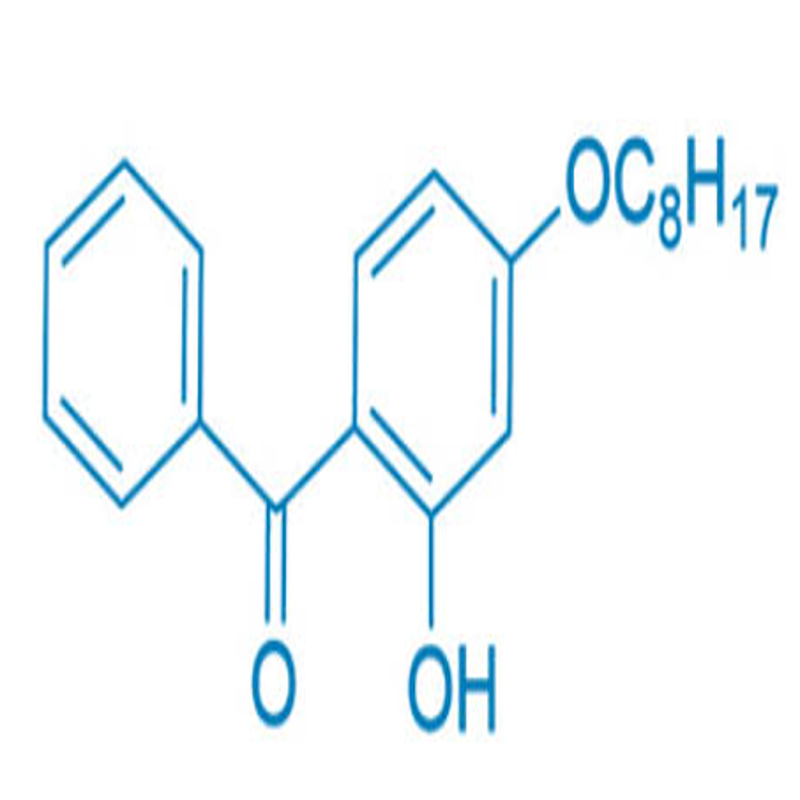
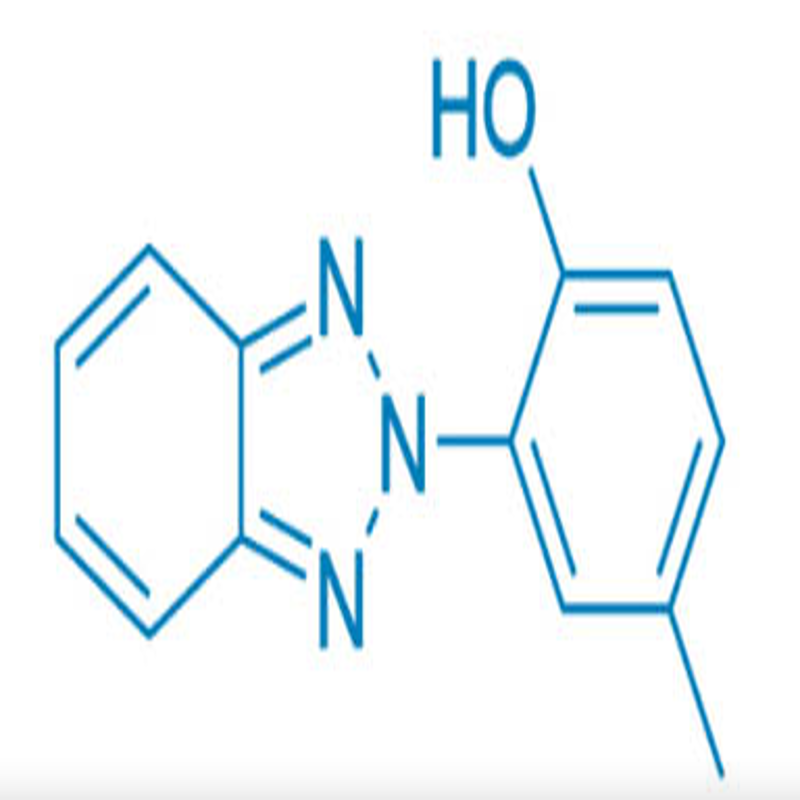
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
According to a new analysis by Wood Mackenzie, more than 650 gigawatts (GW) of new onshore wind capacity and 130 GW of new offshore wind capacity will be installed globally between 2018 and 2028, which will consume more than 5.
5 million tonnes of copper
.
"Wind technology is the most copper-intensive way to generate electricity, and the sector is expected to consume the most copper
over the next decade.
The government has embarked on a shift from reliance on carbon-intensive electricity to more renewable energy
.
As a result, wind and solar have become a popular technology choice," said
Henry Salisbury, research analyst at Wood Mackenzie.
To generate, transmit and distribute electricity, copper is widely used
due to its characteristics such as low resistivity, high conductivity, ductility and durability.
Therefore, copper consumption is expected to grow
significantly over the next decade as society's demand for wind energy increases, expanding its consumption.
"About 58 percent of the copper consumed in wind power facilities is connected
by cable.
Taking into account our current projections for new wind turbine installations between 2018 and 2028, more than 3 million tonnes of copper will be consumed in collector and distribution wiring," Salisbury said
.
According to the report, global wind energy technology is expected to require an average of 450,000 tons of copper per year between 2018 and 2022, before increasing to 600,000 tons
per year by 2028.
China is expected to see the fastest growth in new onshore capacity, consuming 110,000 tonnes of copper per year; This is followed by the United States, which will average 35,000 tons of copper
per year by 2028.
According to a new analysis by Wood Mackenzie, more than 650 gigawatts (GW) of new onshore wind capacity and 130 GW of new offshore wind capacity will be installed globally between 2018 and 2028, which will consume more than 5.
5 million tonnes of copper
.
"Wind technology is the most copper-intensive way to generate electricity, and the sector is expected to consume the most copper
over the next decade.
The government has embarked on a shift from reliance on carbon-intensive electricity to more renewable energy
.
As a result, wind and solar have become a popular technology choice," said
Henry Salisbury, research analyst at Wood Mackenzie.
To generate, transmit and distribute electricity, copper is widely used
due to its characteristics such as low resistivity, high conductivity, ductility and durability.
Therefore, copper consumption is expected to grow
significantly over the next decade as society's demand for wind energy increases, expanding its consumption.
"About 58 percent of the copper consumed in wind power facilities is connected
by cable.
Taking into account our current projections for new wind turbine installations between 2018 and 2028, more than 3 million tonnes of copper will be consumed in collector and distribution wiring," Salisbury said
.
According to the report, global wind energy technology is expected to require an average of 450,000 tons of copper per year between 2018 and 2022, before increasing to 600,000 tons
per year by 2028.
China is expected to see the fastest growth in new onshore capacity, consuming 110,000 tonnes of copper per year; This is followed by the United States, which will average 35,000 tons of copper
per year by 2028.